Prepare yourself for the Microsoft MCSA 70-412 exam. This course explores how to implement an advanced DHCP solution, implement an advanced DNS solution, and deploy and manage IP Address Management.
Videos at the bottom (WinRE)
These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
All, or nearly all, sections include DEMOS so I’m not notating that separately.
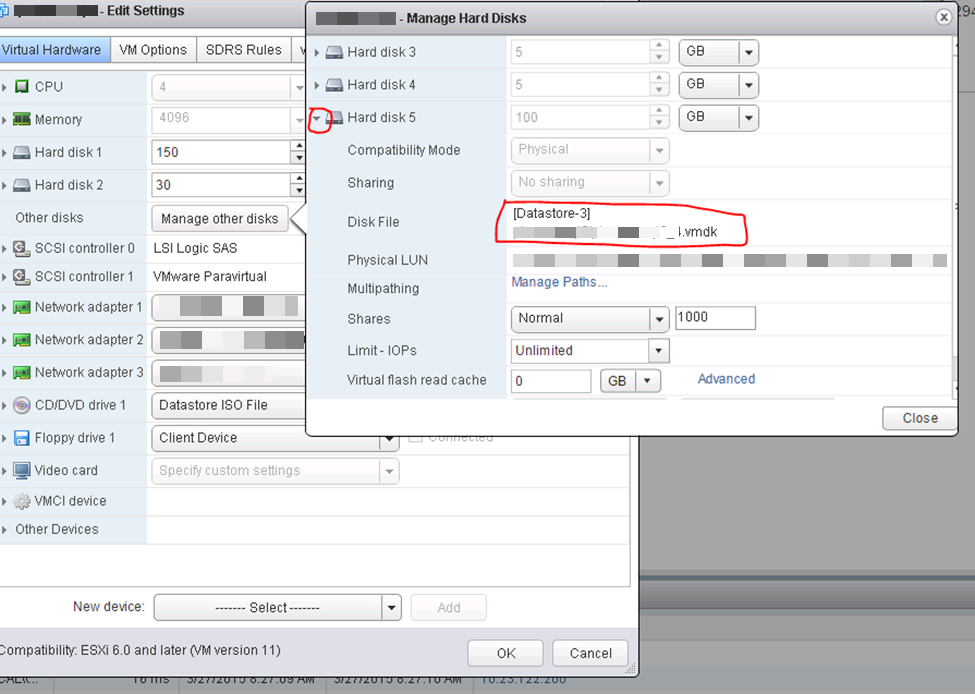
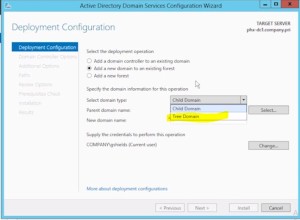
These training courses should be preferably taken in this order (screenshot).
- Configure and Manage Backup Solutions
- Configure Windows Server Backups FEATURE
- Compared to NT backups, this focuses on VOLUMES.
- Pretty fully featured technology today.
- If you want to do Bare Metal backups, you need to check that along with System State, System Reserved, and probably the C or OS drive.
- Advanced settings
- excluded files
- VSS settings
- copy vs. full (are you using some other backup application, if so you use COPY)
- Destination
- local volume
- remote shared folder
- Optimize backup performance = types of backups (full, incremental, etc.)
- POWERSHELL WB = Windows Backup
- Get-WBJob
- Stop-WBJob
- Get-WBVSSBackupOption
- Configure Azure Backups
- designed to just get a back up into the Cloud
- Create “Backup Vault” tied to subscription and choose location
- Download Vault credentials, and download and install Azure Backup Agent
- Is now called MICROSOFT Azure Backup NOT Windows Azure Backup
- set up encryption; Microsoft cannot recover data
- Azure looks almost the same as a Windows backup. File and folder; just data, not system restore.
- Configure role-specific backups
- Backup Operators is the default, maybe too many permissions for many cases; can shut down system.
- Create your own role for backup files and directories and restore files and directories
- Manage VSS settings using VSS Admin
- extended from original design (previous versions for users) to now include backups (quiescence)
- VSS writer (specific by vendor for the application, Exchange, Oracle, AD, SQL, etc.
- the VSS requester is the partner to the writer
- PS vssadmin list writers
- vssadmin list providers
- vssadmin add shadowstorage /for=c: /on=f: /maxsize=20% set location for VSS
- vssadmin create shadow /for=c: create vss shadow copy, very quick nearly instantly
- vssadmin can remove, revert, etc.
- Configure Windows Server Backups FEATURE
- Recover Servers (restore)
- individual file or folder recovery
- backup from – choose location, then choose files and folders (other choices volumes, applications, system state, or virtual machines)
- can put back in same, or different location
- Bare metal server recovery
- boot into WINRE (WINdows Recovery Environment) and also here; Tom’s Guide; when to use RE
- one option is to use shutdown command shutdown /r /o /t 0
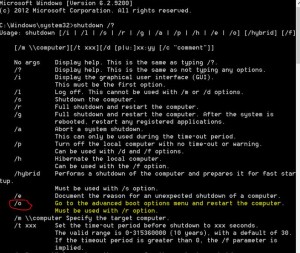 (Check out Windows 8 new shutdown switches here)
(Check out Windows 8 new shutdown switches here) - the /o is a new switch
- This is a gui based windows recovery console. Allows you to find the system image, install drives, connect to network locations to find image. Do you want to repartition drives.
- Don’t even need DVD media.
- Here is a link to a video of the WINRE console.
- The F8 replacement is WINRE
- msconfig – set what startup you get for NEXT boot to boot into safe mode, AD repair, etc. In case boots are so fast you can’t see F8
- you can also boot to windows DVD
- From WINRE you can boot to command prompt view, and you can manipulate unmounted drive (OS is not mounted). You can tell because command prompt is on the X drive which is the WINRE OS
- startrep (start repair scan)
- bootrec (boot record repair) Fixmbr, Fixboot, ScanOS, RebuildBcd
- Advanced boot options (looks like the F8 options)
- safe mode, with networking, with command prompt, boot logging, debugging, low-resolution video, last known good, disable restart, disable early launch anti-malware etc., etc.
- Configure the boot configuration data store
- multi boot menu to offer recovery options (not multi os boot)
- bcdedit
- bcdedit /export c:\save (export and save config)
- one option is to use shutdown command shutdown /r /o /t 0
- boot into WINRE (WINdows Recovery Environment) and also here; Tom’s Guide; when to use RE
- individual file or folder recovery
- Configure site level fault tolerance
- Configure Hyper-V Replica, including Replica Broker and VMs
- Replica is NOT failover clustering
- provides a way to keep another copy of VM files (usually at remote site)
- Replica CAN work with failover clusters
- Replica is NOT OS specific; you can set it up with just shell VM, no OS to prove it
- Kerberos – not encrypted traffic, requires trusted AD
- certs – encrypted, no trusted domain needed
- set up on each VM individually
- configure frequency
- can also set up scheduled recovery points
- VSS for application consistent recovery points
- you can do the initial replication via external media, network, choose other machine, etc.
- set failover TCP/IP
- on the TARGET location server there is “test failover” under network adapter in Hyper-V Manager
- PLANNED failovers all start from the SOURCE location
- UNPLANNED start from Destination location (thought is that the source location is down, or offline)
- Adding Replica to Failover Cluster, need to
- Need to add the Hyper-V Replica Broker ROLE
- Configure Multi Site Clustering, including network settings, Quorum, and Failover Settings
- Configure Hyper-V Replica Extended Replication
- create a second replication site
- this is initiated from the TARGET location of the original source.
- most other stuff is the same
- Configure Global Update Manager
- https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn265972.aspx#BKMK_GUM
- When a state change occurs such as a cluster resource is taken offline, the nodes in a failover cluster must be notified of the change and acknowledge it before the cluster commits the change to the database. The Global Update Manager is responsible for managing these cluster database updates. In Windows Server 2012 R2, you can configure how the cluster manages global updates. By default, the Global Update Manager uses the following modes for failover cluster workloads in Windows Server 2012 R2:
- Recover a Multi Site Failover Cluster
- make sure you can support the IP and network configuration in the failover site
- same Cluster Manager is used to manage stretch (multi site) clusters
- configure preferred owners to deselect the DR site
- QUORUM
- node and file share is preferred
- even number of hosts per location preferred
- Force start without a quorum; https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh270275.aspx
- Configure Hyper-V Replica, including Replica Broker and VMs