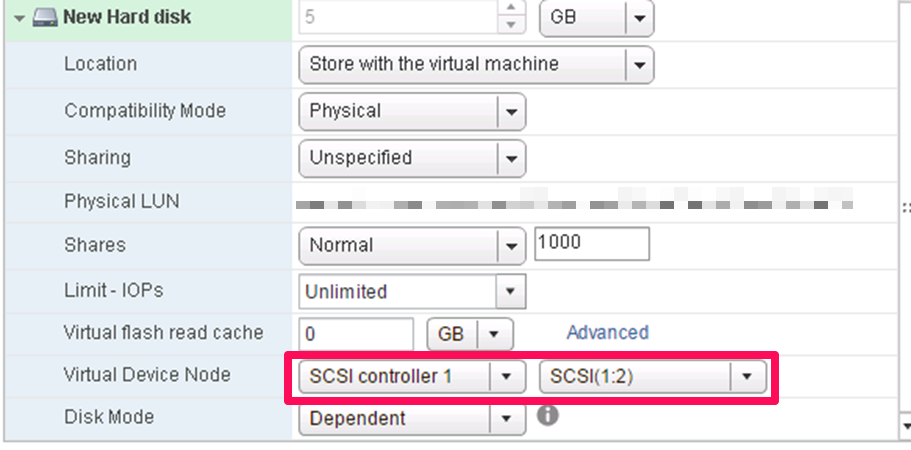
Prepare yourself for the Microsoft MCSA 70-412 exam. This course explores how to implement an advanced DHCP solution, implement an advanced DNS solution, and deploy and manage IP Address Management.
These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
All, or nearly all, sections include DEMOS so I’m not notating that separately.
- Implement an Advanced DHCP Solution
- Create and configure superscopes and multicast scopes
- superscopes – combine multiple DHCP scopes to have broader range of addresses
- initial subnet didn’t have enough addresses
- when you run out of addresses;
- define by geographical location; floor, building, city, etc.
- assign multiple network IPs to router (downside is network admin involvement)
- DHCP RELAY – we’ve been there…allows DHCP traffic to cross router
- DEMO
- In DHCP, create superscope, then add multiple scopes to it
- Multicast scope –
- create Multicast scope, pick start/end IP, set TTL
- unlikely would be allowed on most modern networks
- most common use is WDS or other desktop deployments
- Configure DHCP filters and policies
- nodes in DHCP mmc
- filters; allow or deny by MAC
- then have to “enable” by checkbox
- can set exemptions
- Policies; what options will the managed machines get
- vendor class
- MAC
- FQDN
- Then set what treatment those hosts that fit the policy actually get
- nodes in DHCP mmc
- Implement DHCPv6
- Not a lot of real world use yet
- NOT very simple
- built into IPv6 can auto assign anyhow. Don’t believe it read this article…IPv6 address autoconfiguration
- This would be used for anything beyond what the protocol can do.
- CANNOT assign a default gateway
- CAN assign most other options
- NOT really needed for auto assignment, more used for address control
- DEMO
- click on IPv6, right click “new scope”
- etc. pretty much like IPv4
- beware of test questions about WHY you would use it.
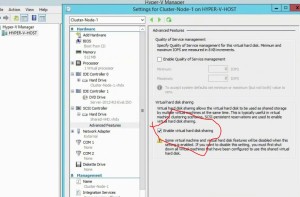
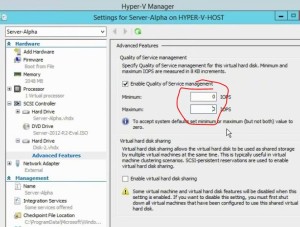
- HA for DHCP – failover and split scopes
- split scopes (the old way)
- 80% / 20% is the most common (I’m sure I’ve seen test questions that said that was wrong though). Well the 80/20 split scope is Microsoft best practice see here.
- Can be messy recovering from a server outage; the DHCP databases don’t know anything about what the other one is doing.
- DHCP Failover
- one DB
- can use 100% of scope
- DEMO
- split scopes (split scope configuration wizard)
- DHCP Failover
- per scope
- “Configure Failover”
- set load balance or hot standby and some other settings
- you can enable message authentication via shared secret
- Configure DNS registration, can discard as well
- split scopes (the old way)
- DHCP Name Protection
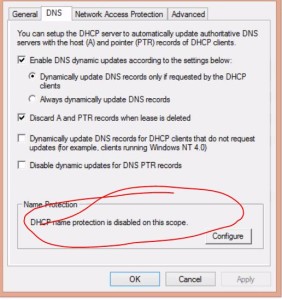
- mainly for non-windows computers (screenshot)
- prevents non-windows from registering a name that is already in use.
- DNS Registration
-
- Configure DNS registration, can discard as well
-
- Create and configure superscopes and multicast scopes
- Implement an Advanced DNS Solution
- Configure Security for DNS, including DNSSEC, DNS Socket Pool, and Cache Locking
- DNSSEC does not necessarily require certs.
- To enable you “sign” the zone.
- Key Master is the authoritative DNS server that generates and manages the key for the zone.
- when you create the new key, then you have all kinds of options
- Needs to be AD integrated zone
- KSK – Key Signing Key and ZSK – Zone Signing Key
- Trust Anchor (for authenticating non-authoritative server
- Then GP is used to tell clients to ask for the DNS key
- “name resolution policy”, checkbox for enable DNSSEC
- create rules to determine who it applies to
- DNS Socket Pool (in response to Kaminsky attack DNS vulnerability)
- randomizes the SOURCE PORT to not be using TCP/53 and UDP/53
- enabled by default, but you tweak settings like number of ports
- DnsCmd /config /socketpoolsize 100000
- DnsCme /info /socketpoolsize
- Cache Locking
- Locks cache after update in cache.
- cannot be overwritting by a percentage of TTL
- default is 100% of TTL
- DnsCmd /config /cachelockingpercent 50
- Configure DNS Logging
- two places it can be configured depending on what you want
- event logging (1) goes into event logs
- debug logging (2) goes into file
- Configure Delegated Administration
- under “security” tab
- for you to delegate activities, you MUST have AD integrated zone (test question?)
- Configure recursion
- disabled by default
- servicing servers outside your network
- should be ON on external server to prevent DNS attacks
- Configure Netmask ordering
- common use – WSUS
- essentially allows DNS server give a client an address that corresponds to the subnet that they are in. For traveling users.
- First response goes to server with same subnet
- Configure Global Names Zone
- for needs that used to be handled by WINS
- short name resolution
- create a zone called “GlobalNames”
- will contain short names
- you have to explicitly enable on all DNS servers
- dnscmd servername /config /enableglobalnamessupport 1
- Analyze Zone level statistics
- Get-DNSServerStatistics -zonename company.local
- DNSLint
- graphical display of internal/external on .htm file
- dnslint
- Configure Security for DNS, including DNSSEC, DNS Socket Pool, and Cache Locking
- Deploy and Manage IP Address Management – IPAM
- Provision IPAM via manual or GP
- IMPORTANT NOTE: to change the IPAM provisioning method (like from manual to automatic) you must UNINSTALL and REINSTALL!
- install FEATURE
- configure from Server Manager
- choose database (internal or SQL)
- GPO Name prefix (manual configuration of IPAM is tedious and not recommended)
- run PS command Invoke-IpamGpoProvisioning -Domain ….creates the Group Policies and links them.
- Run IPAM server discovery
- Choose the ones you want and set them to managed.
- managed servers need to show up in “security filtering’ box on the GPO
- machine has to receive and apply the GP before it shows as “unblocked” and “managed”
- IPAM is more of a “push” instead of pulling in existing IP use
- IP Address block
- 1 or more IP ranges
- Add address range (block of IPs or open range that IPAM can use)
- can add reservations and VIPs
- along with normal DNS, gateway and other information
- Configure server discovery
- create and manage IP blocks and ranges
- migrate to IPAM
- tasks / import IP addresses (imports from .csv). certain mandatory columns for IPAM imports – IPAddress,IPAddressState,AssignmentType,ManagedByService,ServiceInstance,AssetTag
- monitor utilization of IP address space
- lirrlw pie chart by each range, can be adjusted for the entire server
- delegate IPAM administration
- there is an “ACCESS CONTROL” link on the very bottom left to set up roles and access.
- several default roles but you can create your own customized roles and set the policy settings
- Manage IPAM collections
- request new addresses (fine and allocate) “find next”
- RECLAIM ip addresses that are no longer used, delete resource records and DHCP reservations if exist.
- EVENT CATALOG – log viewer of IPAM events
- ADDRESS RANGE GROUPS – group by custom fields you defined during IP creation
- configure IPAM database storage
- PS Move-IPAMDatabase (moved internal IPAM DB to SQL if you want)
- lots of IPAM powershell commands (automation possibilities)