How to create RDM mappings for SQL Clustering with MSCS on VMware 6.0
Using vSphere 6.0
For the sake of this discussion, we’re building two VMs for use in a two node failover MSCS cluster for SQL 2012. We’ll simply call them A and B.
We will be using the Web Client for this, since that’s the direction VMware is pushing. However, the Fat (C#) client is faster for this task as it takes fewer steps. For example, on the fat client, when you create the first RDM mapping, it will automatically create a new, second SCSI controller. When on the web client, you have to manually create the SCSI controller first, then start building the RDM drives.
The documentation in the 6.0 documents is very sparse, and I don’t think it’s even complete or accurate so this took a bit of effort to figure out and get set up.
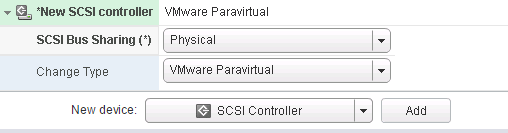
Add a new SCSI Controller (we had issues with other “types” and use VMware Paravirtual exclusively now)
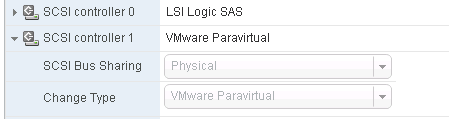
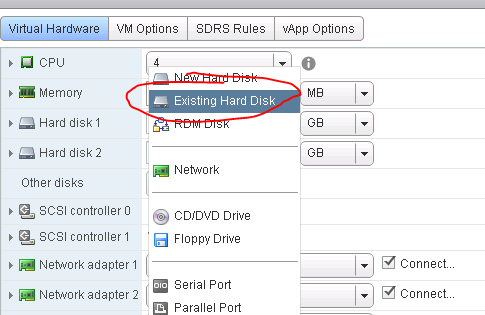
Add a new disk;
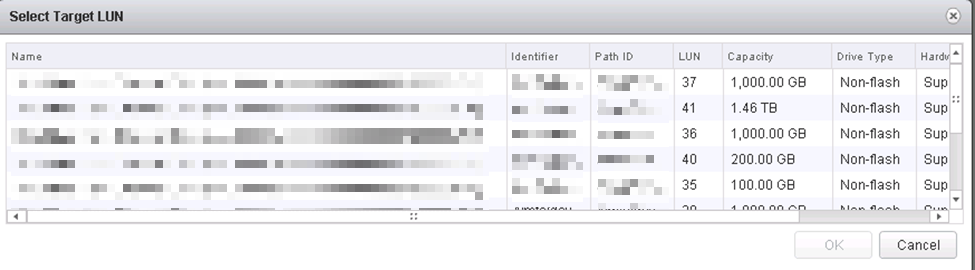
 Select the target LUN by LUN ID;
Select the target LUN by LUN ID;
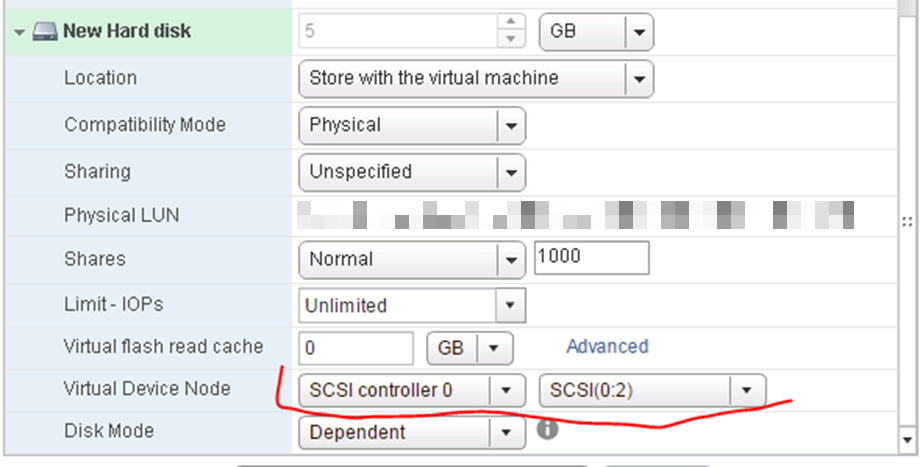
Choose your new SCSI controller 1 (not like picture) and pick an unused SCSI ID.
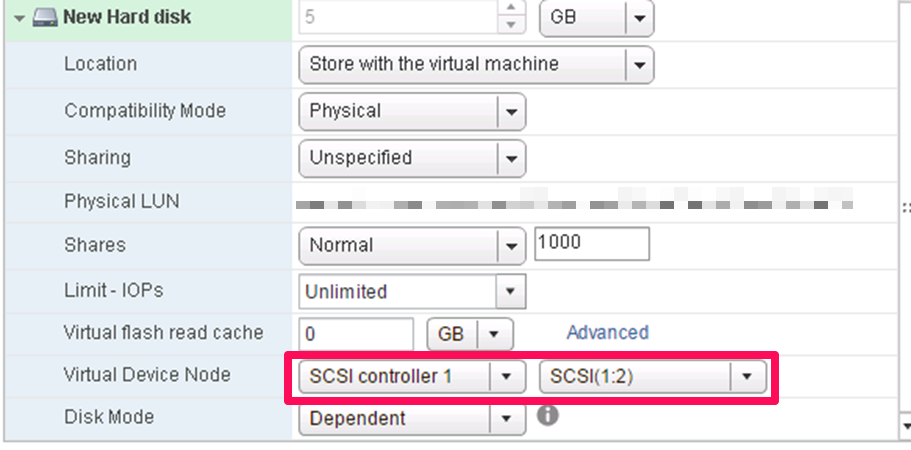
This shows the proper SCSI controller and ID selection.
After creating this, go to the Windows OS on A, bring disk online, initialize, format, name, label, etc.
Now go to server Node B and add a RDM pointing to that exact same file.
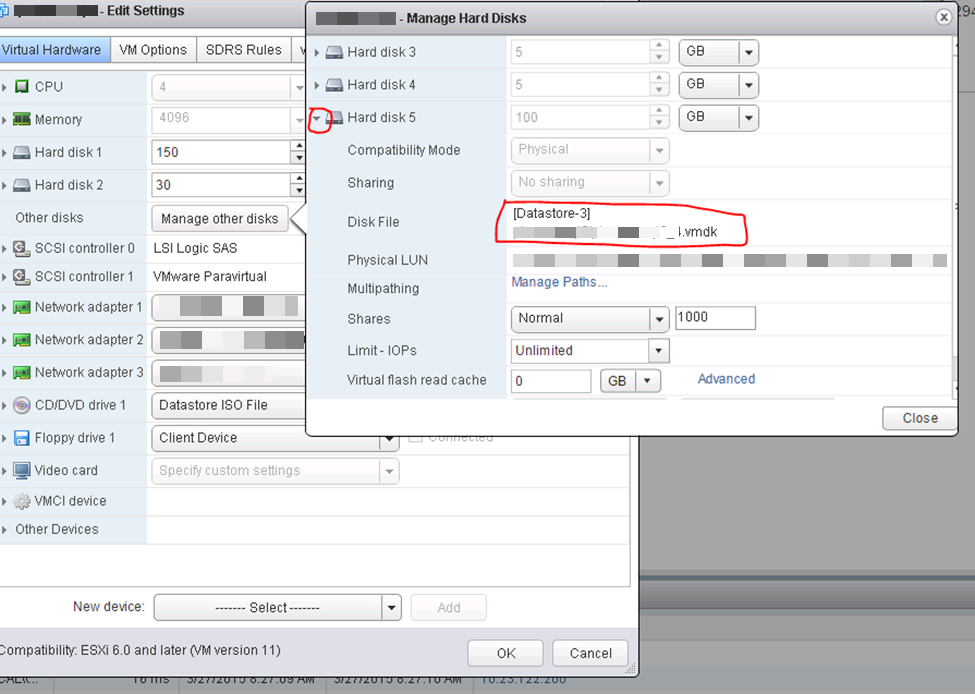
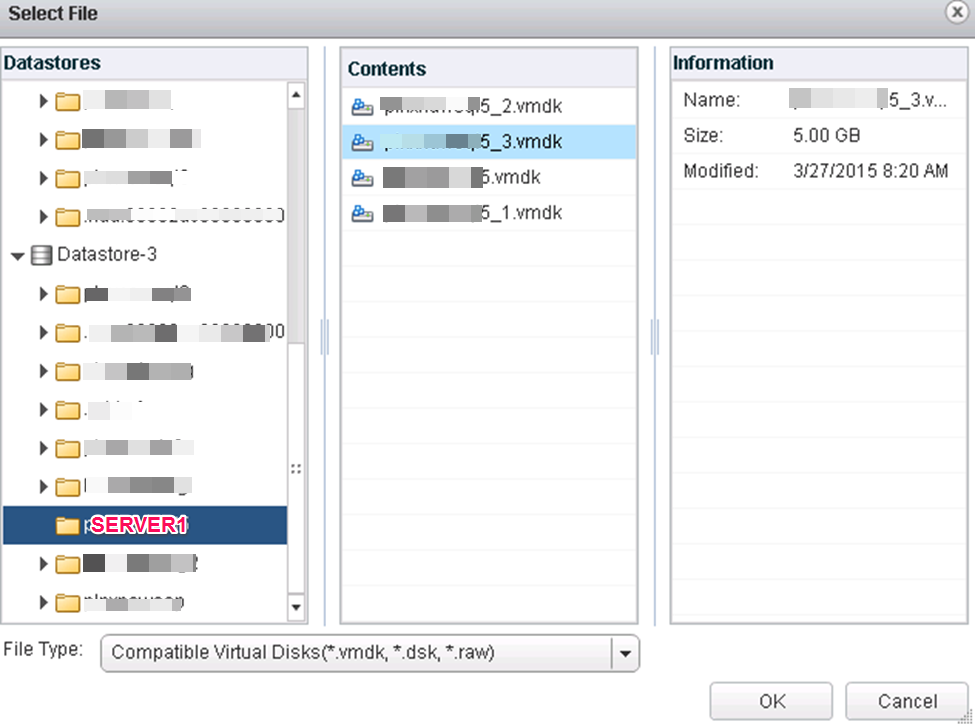
You told it to store the VMDK pointer “with the server” so go to that datastore and fine the VMDK that was created by the new drive creation on A. When you create this drive in VMware on B, then you can go into the OS on the B node and the drive should show up there labeled and formatted and drive lettered.
If you keep track of it as you go, you can add several drives at once on A (2,3,4,5,6,7…) and it will create them all at once, then go over to B and add/create them all at once. But you have to keep your VMDK names and LUN IDs straight so you know which one is which. Doing one at a time is slower but less confusing.
How to tell (after it’s created) which VMDK file a new RDM is using on A, so you can find the correct VMDK when you create B;
Go to “Edit Settings” then at the top there is a “Manage other disks”
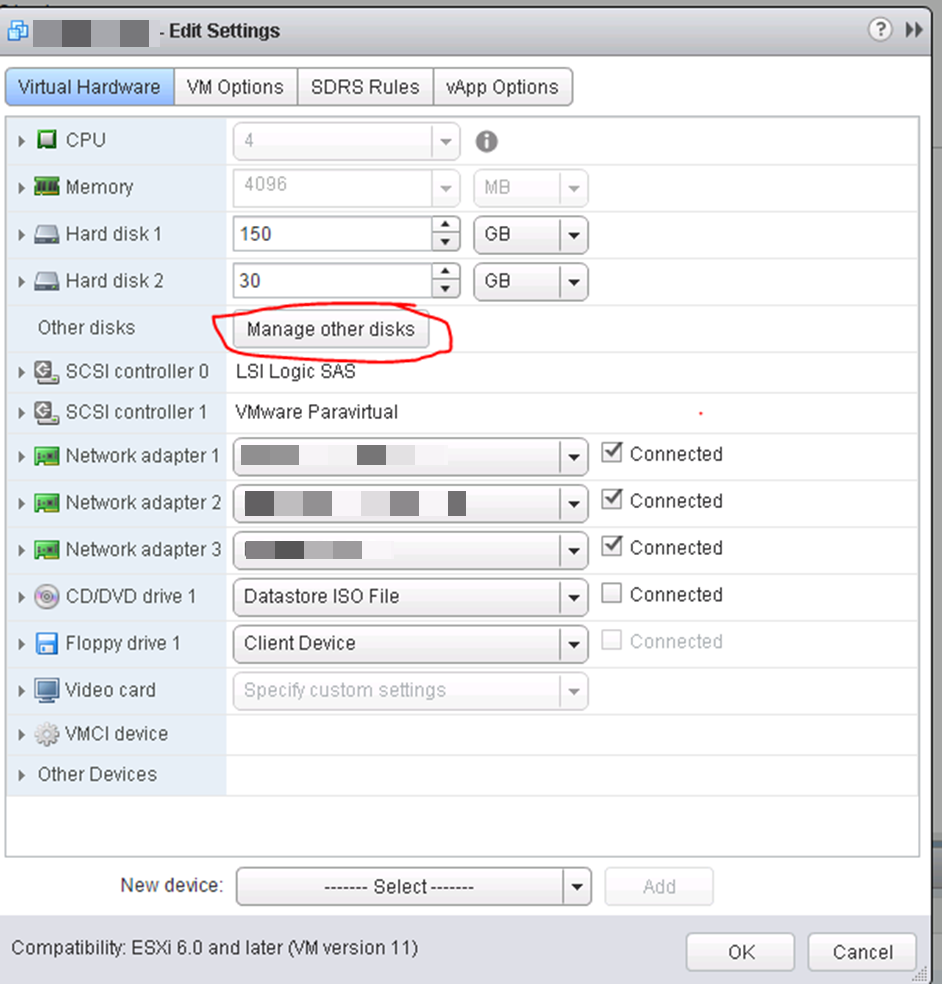
Open that button, then drop down the details on the disk you’re looking at and it will show you the VMDK and datastore. This VMDK is just a “pointer” or “mapping” file to the LUN.
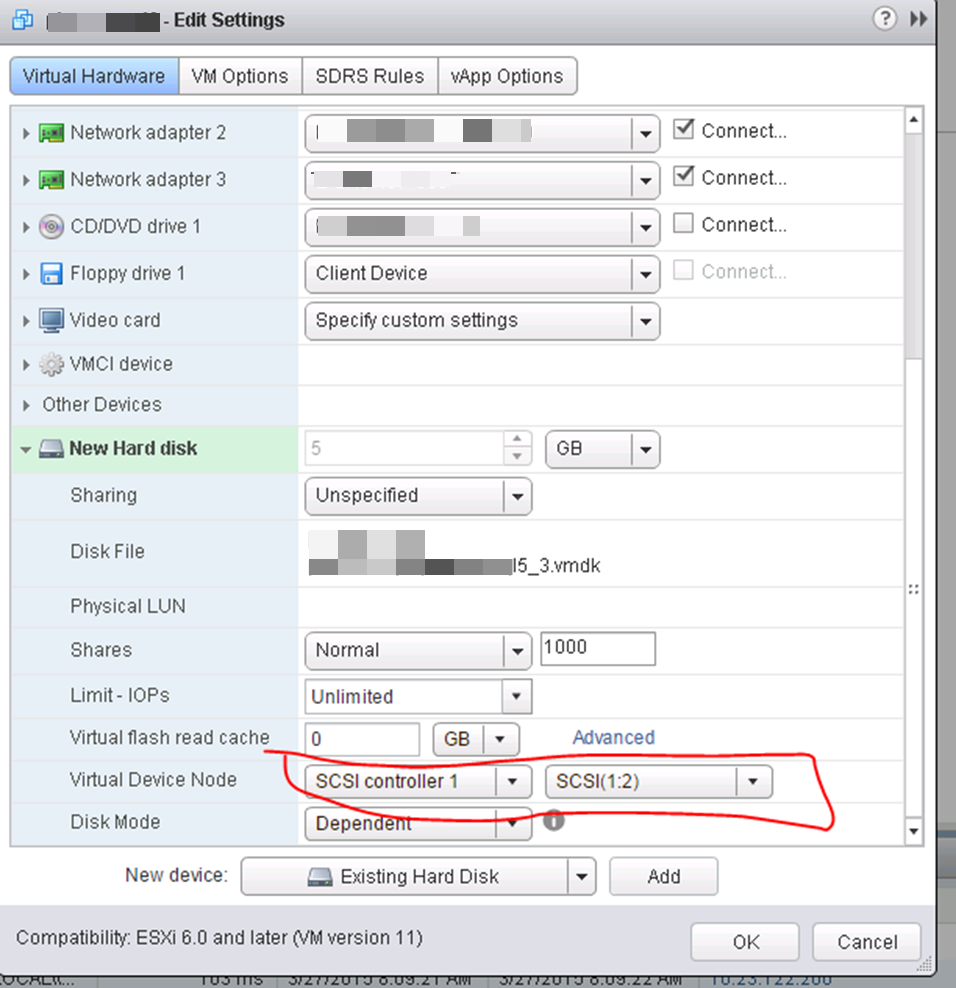
Pick the SAME SCSI controller and port that you did on A;

ISSUES ENCOUNTERED;
Set LUNS as “perennially reserved”. If this is not set right, the ESX HOST will take HOURS to boot, depending on how many RDMs it has to scan. Ours took 2.75 to boot. When this was set right via esxcli, they would boot in about 6 minutes, counting the HP specific boot processes. This is addressed in this KB, scroll down to the “perennially reserved” section. ESXi/ESX hosts with visibility to RDM LUNs being used by MSCS nodes with RDMs may take a long time to start or during LUN rescan (1016106)
EXPANDING RDM sizes.
PARAVIRTUAL driver
Like this:
Like Loading...
 Currently there are lots of problems with the VMware Web Client Integration Plugin as I have noted on LinkedIn. Facing this issue, and having a need to download some files from a datastore to preserve them, you can see a puzzle taking shape. What to do if Flash has crashed your browser(s), and/or the Client Integration Plugin isn’t working? Maybe for some reason you also don’t have the fat client installed and you’re in the middle of an emergency?
Currently there are lots of problems with the VMware Web Client Integration Plugin as I have noted on LinkedIn. Facing this issue, and having a need to download some files from a datastore to preserve them, you can see a puzzle taking shape. What to do if Flash has crashed your browser(s), and/or the Client Integration Plugin isn’t working? Maybe for some reason you also don’t have the fat client installed and you’re in the middle of an emergency?