These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
- Introduction
- Not about the basics, this is 412 training so the basics should be in place
- Multiple Forests, multiple domains
- Configure a Forest or Domain
- Configure Trusts
- Configure Sites (remember from an era when WAN connectivity and site replication was expensive)
- Manage Active Directory and SYSVOL Replication
- RODC
- Configure a Forest or Domain
- implement multi domain and multi forest AD, with interoperability with previous versions of AD.
- Upgrading existing domains and forests, including preparation and functional levels
- Configure multiple UPN suffixes
- Used to require contiguous namespace; contoso.com, denver.contoso.com, paris.contoso.com.
- now we can use DISJOINTED namespaces. can have a forest with the following domains;
- contoso.com
- denver.contoso.com
- widget.com
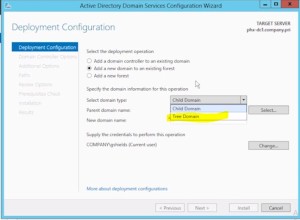
- This is called a TREE DOMAIN (as in “forest”, “trees” I suppose….) vs. the old
CHILD DOMAIN
- now we can use DISJOINTED namespaces. can have a forest with the following domains;
- When would you want to use a multi domain structure (desired state now is to minimize)?
- habit essentially
- political or organizational
- Autonomy (separation)
- Data isolation
- Segregation for replication /authentication /authorization
- SECURITY is not one of the reasons as part of the same forest.
- Multi Forest structure
- when two forests merge (purchase a company, etc.)
- two forests connected by a TRUST of some sort.
- Trusts require MANUAL creation
- Different requirements for AD Schema can dictate multiple Forests
- Exchange Organizations (In Exchange, only allowed one, so if your Exchange needs require more, then you are multi forest)
- Permissions required for creation
- To build a new forest, Local Admin on first DC (there is no AD yet)
- To build a new domain tree or child domain, you must be Enterprise Admin
- To add additional DCs, you must be a Domain Admin
- Upgrade Process for Domain or Forest (know this process)
- get healthy (make sure everything is working right)
- extend the schema (essentially adding columns to AD database, or new characteristics or fields) (ADPREP)
- upgrade DCs to new OS (all DCs need to be upgraded prior to raising functional level). Hopefully you don’t have hundreds of DCs.
- relocate FMSO roles if needed
- raise domain/forest functional level
- DEMO – extend schema
- adprep (link above)
- uses the stack of .ldf files where adprep resides
- remember you can view these attributes in the ad database using ADSI Edit.
- adprep
- first use /forestprep
- then /domain prep
- optionally /gpprep, and /rodcprep
- now raise the functional level
- ad domains and trusts
- cannot go backwords, this is a one way road.
- What’s new in the functional levels
- Creating new UPN suffix
- AD Domains and Trusts, UPN suffixes
- add what you want in AD D and T
- then in ADUC you can use them in the user account tab
- adprep (link above)
- Configure Trusts
- Configure External, Forest, Shortcut, Realm
- Configure trust authentication
- Forest wide, or “selective”
- Configure SID filtering
- Get-ADUser -filter * | select SAMAccountName,sid (returns SIDS for users)
- SID filtering is on my default in external trusts.
- used in domain object migrations (from domain to another)
- has to be turned OFF to migrate (only time you would do this)
- SID history has to be ENABLED to migrate objects, which requires turning off SID filtering. Example; move a user to different domain, if you don’t do this properly a new SID is created and they lose access to printers they used prior. With SID history ENABLED, user object retains a history of both SIDs
- Detailed explanation and example of disabling SID filtering, enabling SID history here.
- Configure Name Suffix Routing
- determine what name suffixes get passed / routed to other side of trust
- Fundamentals
- trusts have direction – trusting, vs. trusted
- the direction is opposite of the direction of access
- remember by “wing it” is ‘eng -> ‘ed. From trustING to trustED.
- most are bi-directional
- can be transitive (if A trusts B, and B trusts C, then A trusts C)
- different types
- External from one domain in one forest to domain in a different forest
- Shortcut – literally a shortcut to another domain in same complex forest. Not common as AD simplifies
- Forest – between two forest roots; everything in forest is trusted. Transitive. Most common type of trust. Acquisitions. Always transitive. Can configure rules of authentication.
- Need name resolution to set up. Can be done by consolidating nameservices. In larger environment, conditional forwarders.
- create from AD Domains and Trusts
- can create both halves of trust from one side (one server)
- Realm trust – to non-AD Kerberos realm / Linux
- Configure Sites
- Created for AD replication across geographical locations
- Associated with subnets (VYOS router for lab)
- KCC (knowledge consistency checker)
- Configure Sites and Subnets
- rename “Default-First-Site-Name”, use it and create additional as needed
- create subnets and associate to sites
- Create and Configure Site Links
- Inter-Site transports
- most of the time is IP, NOT SMTP
- all sites are added to IP default site link
- absolute value of the cost is meaningless, only the RELATIVE value (compared to other links) has meaning
- A lot of this had more meaning when network connectivity was expensive and low capacity
- Manage Site Coverage
- you need a DC in each site
- are the DCs Global Catalogs (old times was limited due to processing power, bandwidth)
- now best practices are simply make every DC a GC
- if multiple DCs in a site, define a preferred BridgeHead server. Or leave this alone and leave it to KCC.
- best practice is leave it to KCC
- Manage Registration of SRV Records
- determines what DC site computers use
- ipconfig -registerdns make the DC set srv records
- Move DCs Between Sites
- Manage AD Replication and SYSVOL replication
- Upgrade SYSVOL replication to DFS-R (Distributed File System Replication)
- If you have an old, upgraded, AD, you might not be on DFS-R and still on the old FRS (File Replication Service)
- upgrading to DFSR
- three steps after get healthy, migrate to prepared state, migrate to redirected state, migrate to eliminated state
- dfsrmig /? (powershell for DFSR migration)
- dfsrmig /getglobalstate
- results will be “prepared”, “redirected”, or “eliminated”
- only do one step at a time then WAIT
- Some health check commands
- gwmi – class win32_logicaldisk – ComputerName yourcomputername (shows drive space)
- repadmin /syncall /force /aped (forces domain sync and ignore all schedules)
- update-DfsrConfigurationFromAD
- Configure replication to RODCs
- single use case; unsecure branch location. only contains passwords and content for that branch
- never log onto RODC with privileged account
- delegated RODC administrator (the selected group can administer the RODC (“managed by” tab)
- Configure password policy replication for RODCs
- set policy for which PWs you want to cache on RODC (password replication TAB)
- you can see what users/computers are replicated to RODC on “advanced” tab.
- Monitor and manage replication
- sites and services – right click and “replicate now” from AD Sites and Services
- repadmin /replicate server1 server2
- repadmin /showrepl
- repadmin /kcc
- repadmin /prp view servername reveal (shows RODC replication)
- in GPMC, look at a domain, you can see replication status
- dfsdiag
- nltest (tests if you can locate a DC)
- AD Change Notification (replicates to all sites instantly)
- ADSI edit
- sites
- “options”, from blank to “1”, now replicates across sites at same replication as intrasite replication.
- Upgrade SYSVOL replication to DFS-R (Distributed File System Replication)