These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
All, or nearly all, sections include DEMOS so I’m not notating that separately.
- Configure Network Load Balancing
- most commonly used with IIS
- stateless (doesn’t matter what node user connects with)
- Configure NLB Prerequisites
- install Feature
- Unicast, Multicast, IGMP Multicast
- Unicast
- always works
- 1:1
- requires a second NIC on each server
- causes subnet flooding; all traffic to all hosts goes to all hosts
- Multicast
- no second NIC
- network configurations
- does not solve subnet flooding
- IGMP Multicast – best practice
- no second nic
- network requirements
- solve subnet flooding problem
- Install NLB Nodes
- Configure Cluster Operation Mode
- Configure Port Rules and Affinity
- Upgrade an NLB Cluster
- Configure Failover Clustering (read prior post here)
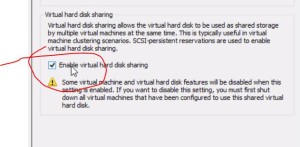
- Cluster Storage
- shared storage is not built in Windows; it’s a foreign concept
- proper configuration of storage is critical
- iSCSI, FC, Storage Spaces (in our previous FS training)
- we’re using iSCSI here in this demo
- Configure Cluster networking
- best practice to separate cluster private network and storage network
- Failover Cluster Manager – console for cluster management
- Cluster Validation wizard (lots of experience with this 😉
- In this Demo, Cluster Private network, Storage network, and Management / Production
- Check the networks in Failover Cluster Manager
- Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) used by Hyper-V virtual machines
- Quorum (chosen by smallest size)
- Available Storage LUNs (if containing a VM, they all would have to fail over at the same time (or each have dedicated LUN)
- CSV, each VM can fail over individually
- you can define a disk as a CSV, and you can revert also.
- More here on Using CSV for Failover Cluster
- CSV cache size configuration; (Get-Cluster).BlockCacheSize = 512 for Server 2012 R2, for more read the link above.
- Quorum configuration
- Quorum is only to identify if enough of a cluster remains to still operate as a quorum.
- Quorum Models (dependent on number of nodes)
- Node majority (used for ODD number of nodes)
- Node and Disk Majority (even number of nodes)
- “split brain” when cluster breaks into two separate groups of nodes who each think they are quorum
- No Majority Disk Only (old, not used any more)
- Node and File Server Majority (special considerations) even nodes, multi site. The separate vote goes to a disk file share somewhere.
- Configure quorum model in Failover Cluster Manager
- MS automatically manages cluster quorum setting now. “use default quorum configuration”
- Or, you can go to advanced features and dance with the complexity on your own.
- Clusters without network names (detached cluster) Deploy an Active Directory-Detached Cluster
- SQL server outside your firewall
- not supported for several additional roles
- no bitlocker
- no CAU (Cluster Aware Updating)
- read the link
- cannot use FOCM
- PS – (Get-Cluster).AdministrativeAccessPoint
- read the link for more
- CAU (Cluster Aware Updating)
- “update cluster” item in Server Manager
- allows cluster to manage resource movement to update nodes/hosts.
- configure self-updating options wizard
- add the ROLE on the cluster
- choose schedule (normal WSUS stuff)
- reboot timeouts, max retries, pre or post scripts, recommended / important
- All the above is for Windows updates, not WSUS
- “Analyze cluster updating readiness”
- PS
- Restoring single node of cluster
- Evict = kicking node out
- restore configuration from backup (make sure you have system state)
- Upgrading a cluster
- not recommended to directly upgrade a cluster
- this is a cut and move
- “copy cluster roles” from a wizard from the TARGET cluster, connect to OLD cluster to get configs.
- Cluster Storage
- Manage Failover Clustering Roles
- remember MSCS is a “general purpose” clustering solution
- role-specific settings
- DFS, SHCP, DTC, FIle Server, iSCSI target, etc., etc..
- Generic application, script, or service
- DEMO – clustered NOTEPAD via Generic Application
- cluster is a SINGLE instance of the app that fails from node to node, moving the resources (including created drives) as needed
- Continuously available file server
- General Use, or SOFS (Scale Out File Server) (used for Hyper-V and SQL)
- Configure Virtual Machines
- do not put SOFS and VMs on same CSV
- fail-over and preferences
- ROLES (shared app, file server, VM, etc.)
- move, stop, change startup priority
- no autostart
- add resources or storage
- “show dependency” report
- graphical representation of dependencies
- “preferred owner” unchecked can be used, just not preferred
- failover max
- failback now/yes, set hours it can happen
- cluster handles DNS records for cluster required records
- you can manually add dependencies
- possible and preferred owners
- possible owners (cannot be on any node that is not checked)
- preferred owner (can use unchecked nodes, they’re just not preferred)
- guest clustering
- Manage VM Movement
- Migration – Live, Quick, Storage
- Quick
- the old fashioned, with a quick period of loss of service
- Live
- no loss of service
- Storage
- moving the .vhdx, the data
- Quick is technically faster, and uses less bandwidth than Live
- Live – procs need to be same manufacturer and similar family
- virtual switches needs to be named the same
- physical devices must be disconnected
- DEMO
- constrained delegation has to be configured to the hosts that you want to migrate to/from
- CredSSP alternative to Kerbos/constrained delegation but CredSSP requires you to log onto the machine to start the migration
- Quick
- Import, Export, Copy
- have to export/import if you can’t do quick/live migration
- Configure VM Health Protection
- move to locations without proper networks, or something similar
- VMHP is under Network Adapter / advanced features
- it will move it back to prior location if it ends up isolated
- ENABLED by default
- Configure Drain on Shutdown
- drain a node on shutdown
- ENABLED by default
- Configure VM Monitoring
- “resources” tab on bottome of Failover Cluster Manager
- checkbox to enable automatic recovery for application health monitoring
- if/when enabled, you can select services via checkbox that you want to include for application monitoring.
- Migration – Live, Quick, Storage