Prepare yourself for the Microsoft MCSA 70-412 exam. This course explores how to implement an advanced DHCP solution, implement an advanced DNS solution, and deploy and manage IP Address Management.
These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
- Install and Configure AD Certificate Services. Essentially setting up internal certificate trusts to mirror, and and can negate the need for, external certificates like Microsoft, Verisign, etc.
- Install an Enterprise Certificate Authority
- The “issuing CA” creates the actual cert file. Issuing CA gets trust from Policy CA, who gets it from a Root CA
- Root is typically standalone, offline. Policy CA standalone or enterprise, typically online. Issuing CA typically enterprise online.
- Issuing CA is the one doing all the day to day work.
- Install CA ROLE, and the Online Responder ROLE
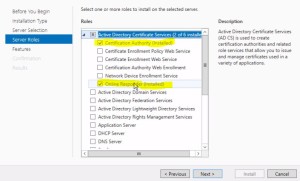
- optional web enrollment pieces, or can use the console to manage
- Post install configuration; configure active directory certificate services, requires member of local admins for some services, and Enterprise Admin for some.
- Decide what TYPE of CA you’re installing.

- Choose a NAME for the CA, usually combination of server name, domain name. Choose validity period (default = 5 years)
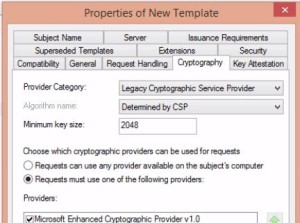
- Certificate Templates – basic templates are provided, then when you fill them out with specific information it creates the actual certificate. Some are “available for issue” then there are dozens of additional ones that are not available for issue by default.
- refresh GP then root cert should be available through AD. certs are automatically trusted by any computer in the domain
- from a client, you can “request a new certificate”, and it automatically enrolls
- Configure CRL (certificate revocation list) Distribution Points
- when you need to manage expiration due to termination, employee leaving, new job responsibilities, etc.
- The CRL location shows up in the “details” tab on the actual cert
- set up CRL revocation list locations BEFORE passing out certs
- you can’t delete crl revocations. Think about it, that makes sense. But when the list gets really long there are ways to make the queries faster.
- Install and Configure Online Responder
- Configure the Online Responder (which also needs a cert) OCSP response signing
- Revocation Configuration for the Online Responder
- Online responder downloads a copy of the CRL to make responses
- enter the URL for the Online Responder in cert templates, and again have this set up prior to issuing any certs or you have to redo them all.
- Implement Administrative Separation
- Principle of Least Privilege
- Read this Technet on Role Based Administration
- In the security tab of the CA, set up the right permissions
- one additional command; PS certutil -setreg ca\RoleSeparationEnabled 1 https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/Cc782357(v=WS.10).aspx
- Configure CA Backup and Recovery
- right click, all tasks, back up and restore recommend private key and logs (checkboxes)
- certutil can also do backups (old way)
- now of course PS Backup-CARoleService
- Install an Enterprise Certificate Authority
- Manage Certificates
- Enrolling for Certificates
- instead of “find cert” start with “request”
- From IIS, you can create request and complete request from wizard on the right side of IIS.
- Example using a PS code signing certificate
- Manage Certificate Templates
- right click / manage, see “code signing certificate”
- copy “duplicate” the template, then modify the new duplicate for use
- publish certificate in AD checkbox
- compatibility settings
- choose encrypt/signature or both
- auto renewal can force a different private key
- WHAT this cert is going to be used for is baked in the cert configuration. For this example signing PS, this would be “code signing”
- “subject name” is usually the FQDN of the webserver. In this case, we specify the user name for our PS signing cert.
- you can configure manager approvals or signatures prior to approval
- security tab; read, enroll, auto-enroll.
- Implement and Manage Certificate Deployment, Validation and Revocation
- now that the template is created, we talk about deployment, validation and revocation
- now you have to right click on Certificate Templates, choose new certificate to issue and find the newly created template to issue.
- revoke certificate from a right click on the cert. This is PERMANENT and not reversible. Note there is a “HOLD” that can be a temporary hold.
- force a CRL update by “publish CRL”
- new crl once a week, new delta crl once a day.
- Configure and Manage Key Archival and Recovery
- there is no default capability to archive keys
- archive when enabled happens in AD
- KRA Key recovery agent cert can recover keys
- copy and modify certificate template
- then you “enroll” for the KRA certificate
- two commands to recover
- PS certutil -GetKey
- certutil -RecoverKey
- Manage Certificate Renewal
- manual non-GPO renewal
- in Certificate console, right click on template, “re-enroll all certificate users”
- Manage Certificate Enrollment and Renewal to Computers and Users using Group Policy
- to auto populate our PS code signing certificate, assigned to our IT group
- GPMC, new GPO
- user side, public key policies
- need certificate enrollment (AD)
- auto-enrollment (enable)
- auto-renewal /log expiry events, other options
- auto renewal is 80% of cert lifespan, or the expiry of the renewal period
- testing on machine, log in, gp runs, check for PS Signing cert
- Configure and Enroll a Hyper-V Replica Certificate
- If you choose replication in Hyper-V and select “encrypt”, then it will error as there is no dedicated custom cert
- copy and rename a “Computer” template
- then make it available for use
- now when you go back to Hyper-V Manager it shows up.
- Enrolling for Certificates
- Install and Configure AD Rights Management Services
- Install a Licensing or Certificate AD RMS Server
- RMS servers are referred to as “cluster”, just meaning multiple servers. You can also do a single server cluster. You need to be Enterprise Admin to complete this setup.
- If you go to a document on File Server, you go to “protect document” then “restrict access” to connect to RMS and “get templates”. Will error if you have no RMS set up.
- Install Active Directory Rights Management Server ROLE.
- Post install configuration is required (yellow alert top right of Server Manager)
- RMS is tied to email field in AD properties general/email field. Even if you don’t have email in reality it just pulls from that field.
- Store RMS Cluster Key (keep this), password, website.
- For location, suggest CName instead of FQDN so you can adapt in the future if the hardware changes.
- Manage AD RMS Service Connection Point
- Manage RMS Templates
- Rights Policy Templates determine what/how you are going to offer to your users.
- example; content that Finance group needs to protect
- Name policy “Finance Protected Content”, add description.
- Tied to the email associated with the finance security group, and you can choose what they can do. Lots of rights / actions, and you can create custom ones as well. view/edit/save/print/save/save as/etc.
- you can disallow client side caching; they would have to be online to access the data
- define revocation policy; when you revoke the license, you revoke the ability to access that policy, you also provide a url where the policy resides.
- Configure Exclusion Policies
- you can determine “Lockbox version exclusion” which is pretty bizarre, read about it on the link.
- Backup and Restore AD RMS
- what do you have to include in backups?
- Configuration DB, directory services DB, logging DB. Either in SQL or the Windows server internal SQL. The internal SQL requires a full server backup. So, from a backup perspective it’s better to use SQL.
- server certificate needs to be backed up
- cluster key password
- export trusted publishing domain
- Install a Licensing or Certificate AD RMS Server
- Implement AD Federation Services – focus seems to be on Workplace Join
- Configure Workplace Join
- understanding Federation
- Traditionally, access is controlled by a user ID and login. Or, from AD permissions.
- Federation is used when access needs to be provided to users OUTSIDE of your domain. (Partner, merger, acquisition, etc.)
- Federation servers handle the federation process between organizations. It’s kind of a bridgehead or gateway for the access request/granting. It does this by generating “claims“.
- Relying Party (us) and Claims Provider (them)
- This happens from a pair of Trusts from each direction; Claims Provider Trust and Relying Party Trust.
- Think also for BYOD situations for non-domain joined devices. Device itself is added to AD.
- Typically connect through Web Application Proxy (not on the 412 test)
- Settings / network / “workplace” is where you see it.. on your desktop, not the server.
- Create a Group Managed Service Account.
- Create a certificate for AD FS
- domain computers needs to have enroll privileges
- Enroll from your AD FS server
- This will require entering additional information to enroll the cert; hostname, DNS name, etc.
- For non-domain devices, it’s a lot easier if you use a public cert, for access and CRL access which is open to non-domain users on the internet.
- understanding Federation
- Install AD FS
- Now create ADFS, create the first server in a federation server farm.
- associate to cert
- name it, add display name
- add service account (use an existing account)
- SQL or internal database.
- finalize the wizard. now you should be the Relying Party Trust.
- Now create ADFS, create the first server in a federation server farm.
- Implement Claims based Authentication including Relying Party Trusts
- in AD FS console, look under Relying Party Trusts to see the claims options.
- Configure Authentication Policies
- from PowerShell
- Initialize-ADDeviceRegistration
- Back in console, enable device authentication in the global policy
- This is just using “windows authentication” instead of Forms based, or other options.
- from PowerShell
- Configure Multi Factor Authentication
- This is a Authentication Policy in the console
- registered/unregistered, intranet/extranet
- now test Workplace Join from desktop. You just click “join” and it’s joined. Button changes from “join” to “leave”.
- Configure Workplace Join