These guys deserve some props for their Services Security Editor; from Core Technologies. It works 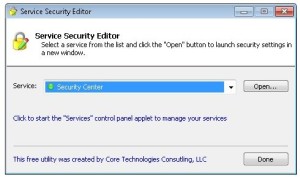 really well to modify permissions on services. For example, you have a developer who only has RDP access to a server, but you want him to be able to restart ONE single service he supports. This is the tool. Think of SUBINACL with a GUI! http://www.coretechnologies.com/products/ServiceSecurityEditor/
really well to modify permissions on services. For example, you have a developer who only has RDP access to a server, but you want him to be able to restart ONE single service he supports. This is the tool. Think of SUBINACL with a GUI! http://www.coretechnologies.com/products/ServiceSecurityEditor/
List of FREE courses on Pluralsight
Course subscriptions
- Advanced Modeling Tools in Revit
- Age Progression in Photoshop
- Agile Fundamentals
- C# Concurrent Collections
- C# Fundamentals with C# 5.0
- Careers in IT: How to Get Your First Job
- Cisco CCNA: Introduction to Networking
- Creating a Mobile Puzzle Game in Unity
- Creating a Multi-Page Brochure Layout in InDesign
- Creating a UI/UX Motion Study in After Effects
- Creating Responsive Landing Pages in Photoshop and CSS
- Docker Deep Dive
- Drawing and Painting in Illustrator
- Ethical Hacking: Understanding Ethical Hacking
- Hosting SQL Server in Microsoft Azure IaaS Fundamentals
- IDisposable Best Practices for C# Developers
- Introduction to Axure
- Introduction to MoGraph in CINEMA 4D
- Introduction to Testing in Java
- Introduction to Virtualization
- Introduction to Windows Azure Infrastructure as a Service
- JavaScript Build Automation With Gulp.js
- jQuery Advanced Topics
- Learning Technology in the Information Age
- Lighting a Scene for Feature Film with V-Ray in Maya
- Linux System Administration Fundamentals
- Microsoft Azure Administration New Features (March 2014)
- Play By Play: Azure Deployment with Scott Hanselman
- Play by Play: Azure Security with Mark Russinovich
- Play by Play: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript with Lea Verou
- Play by Play: JitJea with Jeffrey Snover
- PMP® – Introduction to Project Management & the PMP® Exam
- PowerShell v3/v4 Essentials for IT Admins Part 1
- Practical Networking
- Quick Start to Unreal Engine 4: Volume 1
- SQL Server on Microsoft Azure IaaS – Optimizations & High Availability
- System Center 2012 R2 Self Service Virtual Machine Provisioning
- Tactical Design Patterns in .NET: Managing Responsibilities
- The Dark Side of Technology Careers
- Understanding the Difference Between Microsoft Azure and Amazon AWS
- Understanding the Java Virtual Machine: Memory Management
- User Experience Flow Modeling for Portfolio Websites in Photoshop
- Windows Azure Infrastructure as a Service Essentials
- Windows PowerShell Desired State Configuration Fundamentals
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-410) Install and Configure Servers
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) Configure Active Directory
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) Configure High Availability
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) Configure Network Services
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) Continuity and Disaster Recovery
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) File and Storage Solutions
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) Identity and Access Solutions
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) MCSA and the 70-412 Exam
- Windows Server 2012 R2 New Features
- Windows Server vNext First Look
Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) Continuity and Disaster Recovery – Study Guide
Prepare yourself for the Microsoft MCSA 70-412 exam. This course explores how to implement an advanced DHCP solution, implement an advanced DNS solution, and deploy and manage IP Address Management.
Videos at the bottom (WinRE)
These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
All, or nearly all, sections include DEMOS so I’m not notating that separately.
These training courses should be preferably taken in this order (screenshot).
- Configure and Manage Backup Solutions
- Configure Windows Server Backups FEATURE
- Compared to NT backups, this focuses on VOLUMES.
- Pretty fully featured technology today.
- If you want to do Bare Metal backups, you need to check that along with System State, System Reserved, and probably the C or OS drive.
- Advanced settings
- excluded files
- VSS settings
- copy vs. full (are you using some other backup application, if so you use COPY)
- Destination
- local volume
- remote shared folder
- Optimize backup performance = types of backups (full, incremental, etc.)
- POWERSHELL WB = Windows Backup
- Get-WBJob
- Stop-WBJob
- Get-WBVSSBackupOption
- Configure Azure Backups
- designed to just get a back up into the Cloud
- Create “Backup Vault” tied to subscription and choose location
- Download Vault credentials, and download and install Azure Backup Agent
- Is now called MICROSOFT Azure Backup NOT Windows Azure Backup
- set up encryption; Microsoft cannot recover data
- Azure looks almost the same as a Windows backup. File and folder; just data, not system restore.
- Configure role-specific backups
- Backup Operators is the default, maybe too many permissions for many cases; can shut down system.
- Create your own role for backup files and directories and restore files and directories
- Manage VSS settings using VSS Admin
- extended from original design (previous versions for users) to now include backups (quiescence)
- VSS writer (specific by vendor for the application, Exchange, Oracle, AD, SQL, etc.
- the VSS requester is the partner to the writer
- PS vssadmin list writers
- vssadmin list providers
- vssadmin add shadowstorage /for=c: /on=f: /maxsize=20% set location for VSS
- vssadmin create shadow /for=c: create vss shadow copy, very quick nearly instantly
- vssadmin can remove, revert, etc.
- Configure Windows Server Backups FEATURE
- Recover Servers (restore)
- individual file or folder recovery
- backup from – choose location, then choose files and folders (other choices volumes, applications, system state, or virtual machines)
- can put back in same, or different location
- Bare metal server recovery
- boot into WINRE (WINdows Recovery Environment) and also here; Tom’s Guide; when to use RE
- one option is to use shutdown command shutdown /r /o /t 0
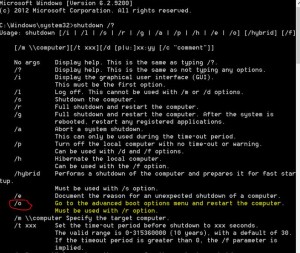 (Check out Windows 8 new shutdown switches here)
(Check out Windows 8 new shutdown switches here) - the /o is a new switch
- This is a gui based windows recovery console. Allows you to find the system image, install drives, connect to network locations to find image. Do you want to repartition drives.
- Don’t even need DVD media.
- Here is a link to a video of the WINRE console.
- The F8 replacement is WINRE
- msconfig – set what startup you get for NEXT boot to boot into safe mode, AD repair, etc. In case boots are so fast you can’t see F8
- you can also boot to windows DVD
- From WINRE you can boot to command prompt view, and you can manipulate unmounted drive (OS is not mounted). You can tell because command prompt is on the X drive which is the WINRE OS
- startrep (start repair scan)
- bootrec (boot record repair) Fixmbr, Fixboot, ScanOS, RebuildBcd
- Advanced boot options (looks like the F8 options)
- safe mode, with networking, with command prompt, boot logging, debugging, low-resolution video, last known good, disable restart, disable early launch anti-malware etc., etc.
- Configure the boot configuration data store
- multi boot menu to offer recovery options (not multi os boot)
- bcdedit
- bcdedit /export c:\save (export and save config)
- one option is to use shutdown command shutdown /r /o /t 0
- boot into WINRE (WINdows Recovery Environment) and also here; Tom’s Guide; when to use RE
- individual file or folder recovery
- Configure site level fault tolerance
- Configure Hyper-V Replica, including Replica Broker and VMs
- Replica is NOT failover clustering
- provides a way to keep another copy of VM files (usually at remote site)
- Replica CAN work with failover clusters
- Replica is NOT OS specific; you can set it up with just shell VM, no OS to prove it
- Kerberos – not encrypted traffic, requires trusted AD
- certs – encrypted, no trusted domain needed
- set up on each VM individually
- configure frequency
- can also set up scheduled recovery points
- VSS for application consistent recovery points
- you can do the initial replication via external media, network, choose other machine, etc.
- set failover TCP/IP
- on the TARGET location server there is “test failover” under network adapter in Hyper-V Manager
- PLANNED failovers all start from the SOURCE location
- UNPLANNED start from Destination location (thought is that the source location is down, or offline)
- Adding Replica to Failover Cluster, need to
- Need to add the Hyper-V Replica Broker ROLE
- Configure Multi Site Clustering, including network settings, Quorum, and Failover Settings
- Configure Hyper-V Replica Extended Replication
- create a second replication site
- this is initiated from the TARGET location of the original source.
- most other stuff is the same
- Configure Global Update Manager
- https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn265972.aspx#BKMK_GUM
- When a state change occurs such as a cluster resource is taken offline, the nodes in a failover cluster must be notified of the change and acknowledge it before the cluster commits the change to the database. The Global Update Manager is responsible for managing these cluster database updates. In Windows Server 2012 R2, you can configure how the cluster manages global updates. By default, the Global Update Manager uses the following modes for failover cluster workloads in Windows Server 2012 R2:
- Recover a Multi Site Failover Cluster
- make sure you can support the IP and network configuration in the failover site
- same Cluster Manager is used to manage stretch (multi site) clusters
- configure preferred owners to deselect the DR site
- QUORUM
- node and file share is preferred
- even number of hosts per location preferred
- Force start without a quorum; https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh270275.aspx
- Configure Hyper-V Replica, including Replica Broker and VMs
Installing Hyper-V Role in VMware Workstation; error Hyper-V cannot be installed: A hypervisor is already running
This quick post and video shows how to get past the Hyper-V cannot be installed: “A hypervisor is 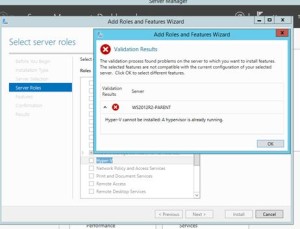 already running” error when trying to install the Hyper-V Role on a server running as a VM on VMware Workstation. This is common in a virtual lap scenario for certification study.
already running” error when trying to install the Hyper-V Role on a server running as a VM on VMware Workstation. This is common in a virtual lap scenario for certification study.
- Shut down the virtual machine.
- Click Virtual machine > Settings.
- Select General and change the guest OS type to Hyper-V (unsupported).
- Select Processors & Memory in the Settings.
- In the Advanced options of Processors & Memory, select Enable hypervisor applications in the virtual machine
- Reboot the virtual machine to enable Hyper-V.
The video is here
Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) Configure Network Services – Study Guide
Prepare yourself for the Microsoft MCSA 70-412 exam. This course explores how to implement an advanced DHCP solution, implement an advanced DNS solution, and deploy and manage IP Address Management.
These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
All, or nearly all, sections include DEMOS so I’m not notating that separately.
- Implement an Advanced DHCP Solution
- Create and configure superscopes and multicast scopes
- superscopes – combine multiple DHCP scopes to have broader range of addresses
- initial subnet didn’t have enough addresses
- when you run out of addresses;
- define by geographical location; floor, building, city, etc.
- assign multiple network IPs to router (downside is network admin involvement)
- DHCP RELAY – we’ve been there…allows DHCP traffic to cross router
- DEMO
- In DHCP, create superscope, then add multiple scopes to it
- Multicast scope –
- create Multicast scope, pick start/end IP, set TTL
- unlikely would be allowed on most modern networks
- most common use is WDS or other desktop deployments
- Configure DHCP filters and policies
- nodes in DHCP mmc
- filters; allow or deny by MAC
- then have to “enable” by checkbox
- can set exemptions
- Policies; what options will the managed machines get
- vendor class
- MAC
- FQDN
- Then set what treatment those hosts that fit the policy actually get
- nodes in DHCP mmc
- Implement DHCPv6
- Not a lot of real world use yet
- NOT very simple
- built into IPv6 can auto assign anyhow. Don’t believe it read this article…IPv6 address autoconfiguration
- This would be used for anything beyond what the protocol can do.
- CANNOT assign a default gateway
- CAN assign most other options
- NOT really needed for auto assignment, more used for address control
- DEMO
- click on IPv6, right click “new scope”
- etc. pretty much like IPv4
- beware of test questions about WHY you would use it.
- HA for DHCP – failover and split scopes
- split scopes (the old way)
- 80% / 20% is the most common (I’m sure I’ve seen test questions that said that was wrong though). Well the 80/20 split scope is Microsoft best practice see here.
- Can be messy recovering from a server outage; the DHCP databases don’t know anything about what the other one is doing.
- DHCP Failover
- one DB
- can use 100% of scope
- DEMO
- split scopes (split scope configuration wizard)
- DHCP Failover
- per scope
- “Configure Failover”
- set load balance or hot standby and some other settings
- you can enable message authentication via shared secret
- Configure DNS registration, can discard as well
- split scopes (the old way)
- DHCP Name Protection
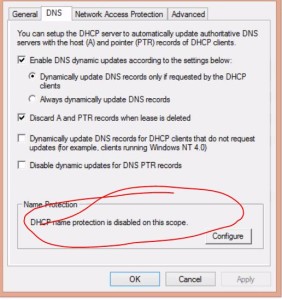
- mainly for non-windows computers (screenshot)
- prevents non-windows from registering a name that is already in use.
- DNS Registration
-
- Configure DNS registration, can discard as well
-
- Create and configure superscopes and multicast scopes
- Implement an Advanced DNS Solution
- Configure Security for DNS, including DNSSEC, DNS Socket Pool, and Cache Locking
- DNSSEC does not necessarily require certs.
- To enable you “sign” the zone.
- Key Master is the authoritative DNS server that generates and manages the key for the zone.
- when you create the new key, then you have all kinds of options
- Needs to be AD integrated zone
- KSK – Key Signing Key and ZSK – Zone Signing Key
- Trust Anchor (for authenticating non-authoritative server
- Then GP is used to tell clients to ask for the DNS key
- “name resolution policy”, checkbox for enable DNSSEC
- create rules to determine who it applies to
- DNS Socket Pool (in response to Kaminsky attack DNS vulnerability)
- randomizes the SOURCE PORT to not be using TCP/53 and UDP/53
- enabled by default, but you tweak settings like number of ports
- DnsCmd /config /socketpoolsize 100000
- DnsCme /info /socketpoolsize
- Cache Locking
- Locks cache after update in cache.
- cannot be overwritting by a percentage of TTL
- default is 100% of TTL
- DnsCmd /config /cachelockingpercent 50
- Configure DNS Logging
- two places it can be configured depending on what you want
- event logging (1) goes into event logs
- debug logging (2) goes into file
- Configure Delegated Administration
- under “security” tab
- for you to delegate activities, you MUST have AD integrated zone (test question?)
- Configure recursion
- disabled by default
- servicing servers outside your network
- should be ON on external server to prevent DNS attacks
- Configure Netmask ordering
- common use – WSUS
- essentially allows DNS server give a client an address that corresponds to the subnet that they are in. For traveling users.
- First response goes to server with same subnet
- Configure Global Names Zone
- for needs that used to be handled by WINS
- short name resolution
- create a zone called “GlobalNames”
- will contain short names
- you have to explicitly enable on all DNS servers
- dnscmd servername /config /enableglobalnamessupport 1
- Analyze Zone level statistics
- Get-DNSServerStatistics -zonename company.local
- DNSLint
- graphical display of internal/external on .htm file
- dnslint
- Configure Security for DNS, including DNSSEC, DNS Socket Pool, and Cache Locking
- Deploy and Manage IP Address Management – IPAM
- Provision IPAM via manual or GP
- IMPORTANT NOTE: to change the IPAM provisioning method (like from manual to automatic) you must UNINSTALL and REINSTALL!
- install FEATURE
- configure from Server Manager
- choose database (internal or SQL)
- GPO Name prefix (manual configuration of IPAM is tedious and not recommended)
- run PS command Invoke-IpamGpoProvisioning -Domain ….creates the Group Policies and links them.
- Run IPAM server discovery
- Choose the ones you want and set them to managed.
- managed servers need to show up in “security filtering’ box on the GPO
- machine has to receive and apply the GP before it shows as “unblocked” and “managed”
- IPAM is more of a “push” instead of pulling in existing IP use
- IP Address block
- 1 or more IP ranges
- Add address range (block of IPs or open range that IPAM can use)
- can add reservations and VIPs
- along with normal DNS, gateway and other information
- Configure server discovery
- create and manage IP blocks and ranges
- migrate to IPAM
- tasks / import IP addresses (imports from .csv). certain mandatory columns for IPAM imports – IPAddress,IPAddressState,AssignmentType,ManagedByService,ServiceInstance,AssetTag
- monitor utilization of IP address space
- lirrlw pie chart by each range, can be adjusted for the entire server
- delegate IPAM administration
- there is an “ACCESS CONTROL” link on the very bottom left to set up roles and access.
- several default roles but you can create your own customized roles and set the policy settings
- Manage IPAM collections
- request new addresses (fine and allocate) “find next”
- RECLAIM ip addresses that are no longer used, delete resource records and DHCP reservations if exist.
- EVENT CATALOG – log viewer of IPAM events
- ADDRESS RANGE GROUPS – group by custom fields you defined during IP creation
- configure IPAM database storage
- PS Move-IPAMDatabase (moved internal IPAM DB to SQL if you want)
- lots of IPAM powershell commands (automation possibilities)
How to create RDM mappings for SQL Clustering with MSCS on VMware 6.0
How to create RDM mappings for SQL Clustering with MSCS on VMware 6.0
Using vSphere 6.0
For the sake of this discussion, we’re building two VMs for use in a two node failover MSCS cluster for SQL 2012. We’ll simply call them A and B.
We will be using the Web Client for this, since that’s the direction VMware is pushing. However, the Fat (C#) client is faster for this task as it takes fewer steps. For example, on the fat client, when you create the first RDM mapping, it will automatically create a new, second SCSI controller. When on the web client, you have to manually create the SCSI controller first, then start building the RDM drives.
The documentation in the 6.0 documents is very sparse, and I don’t think it’s even complete or accurate so this took a bit of effort to figure out and get set up.
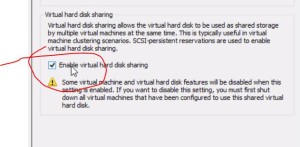
Add a new SCSI Controller (we had issues with other “types” and use VMware Paravirtual exclusively now)
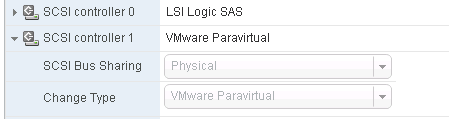
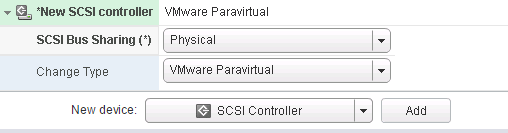
Add a new disk;
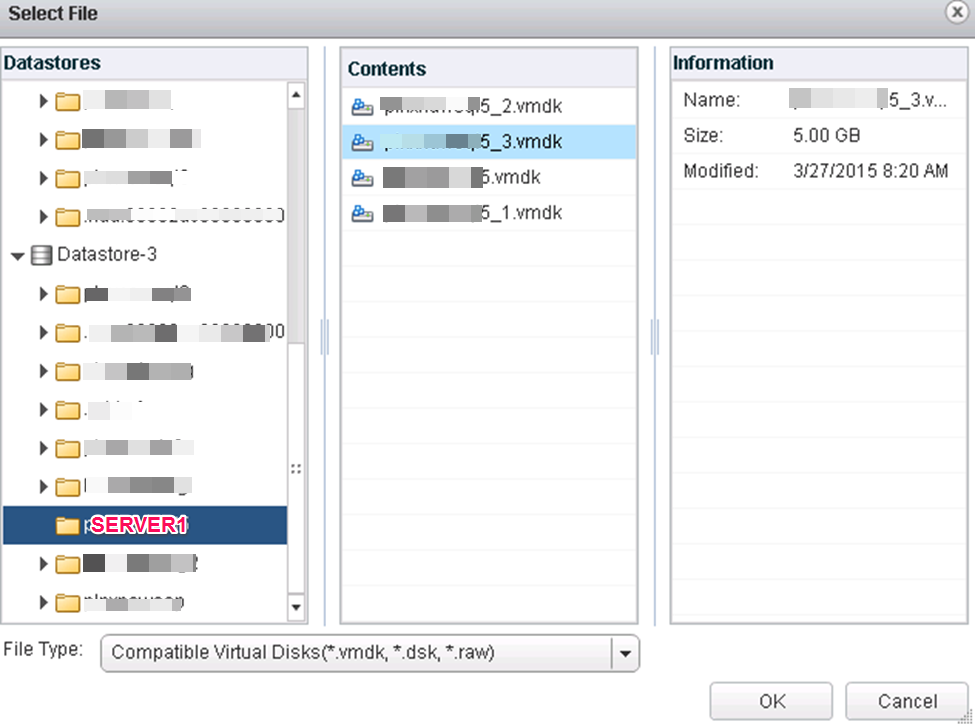
![]() Select the target LUN by LUN ID;
Select the target LUN by LUN ID;
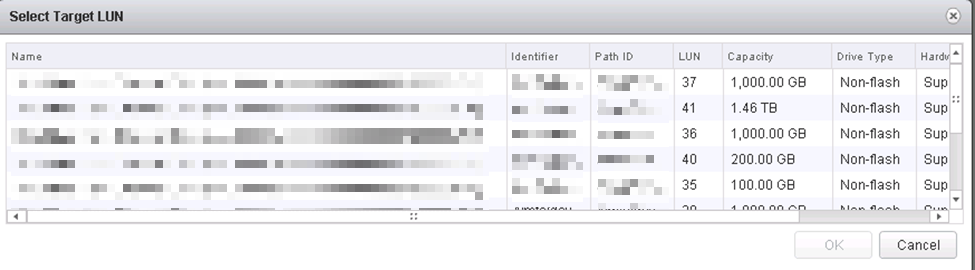
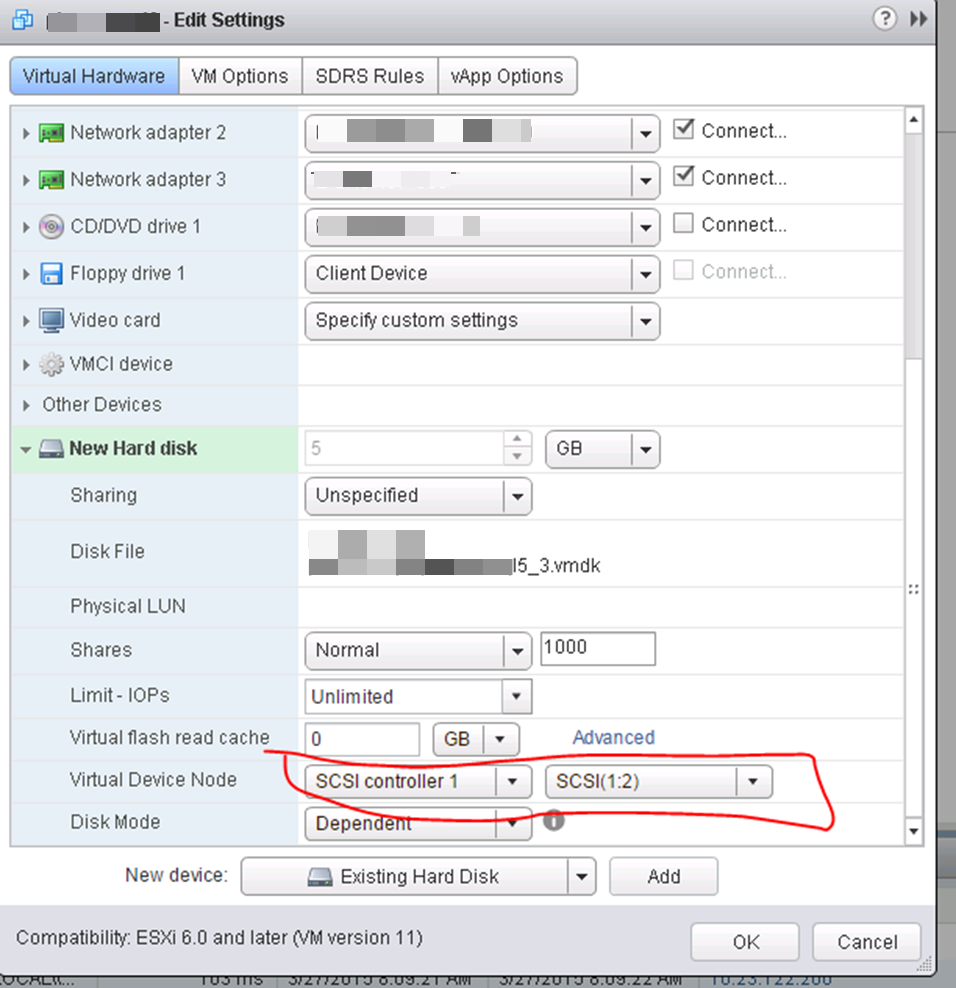
Choose your new SCSI controller 1 (not like picture) and pick an unused SCSI ID.
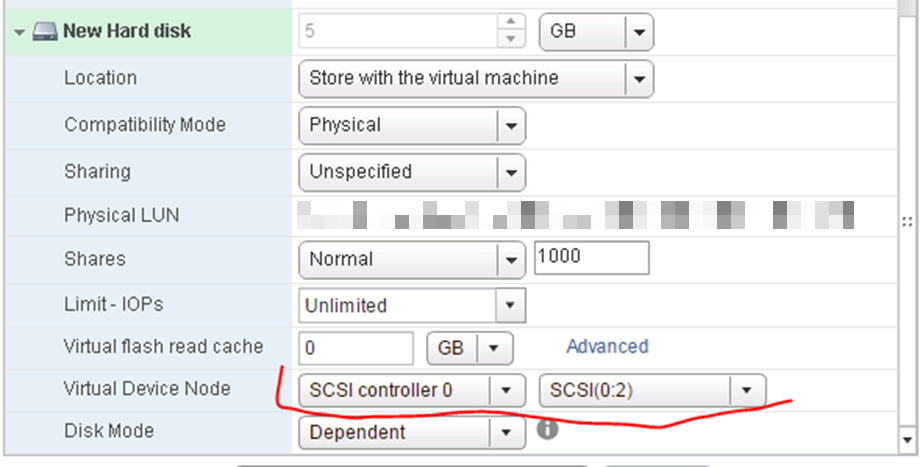
This shows the proper SCSI controller and ID selection.
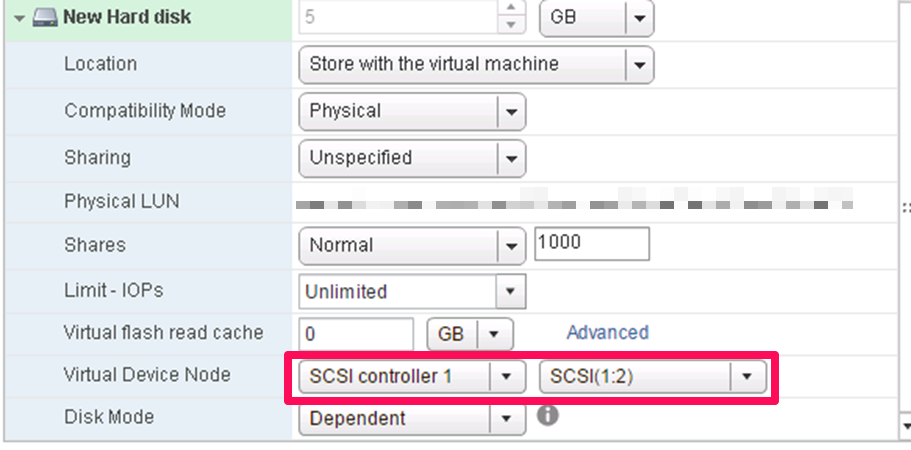
After creating this, go to the Windows OS on A, bring disk online, initialize, format, name, label, etc.
Now go to server Node B and add a RDM pointing to that exact same file.
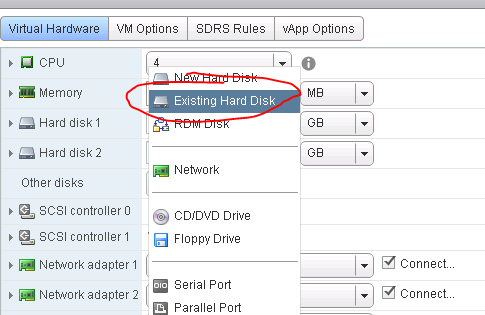
You told it to store the VMDK pointer “with the server” so go to that datastore and fine the VMDK that was created by the new drive creation on A. When you create this drive in VMware on B, then you can go into the OS on the B node and the drive should show up there labeled and formatted and drive lettered.
If you keep track of it as you go, you can add several drives at once on A (2,3,4,5,6,7…) and it will create them all at once, then go over to B and add/create them all at once. But you have to keep your VMDK names and LUN IDs straight so you know which one is which. Doing one at a time is slower but less confusing.
How to tell (after it’s created) which VMDK file a new RDM is using on A, so you can find the correct VMDK when you create B;
Go to “Edit Settings” then at the top there is a “Manage other disks”
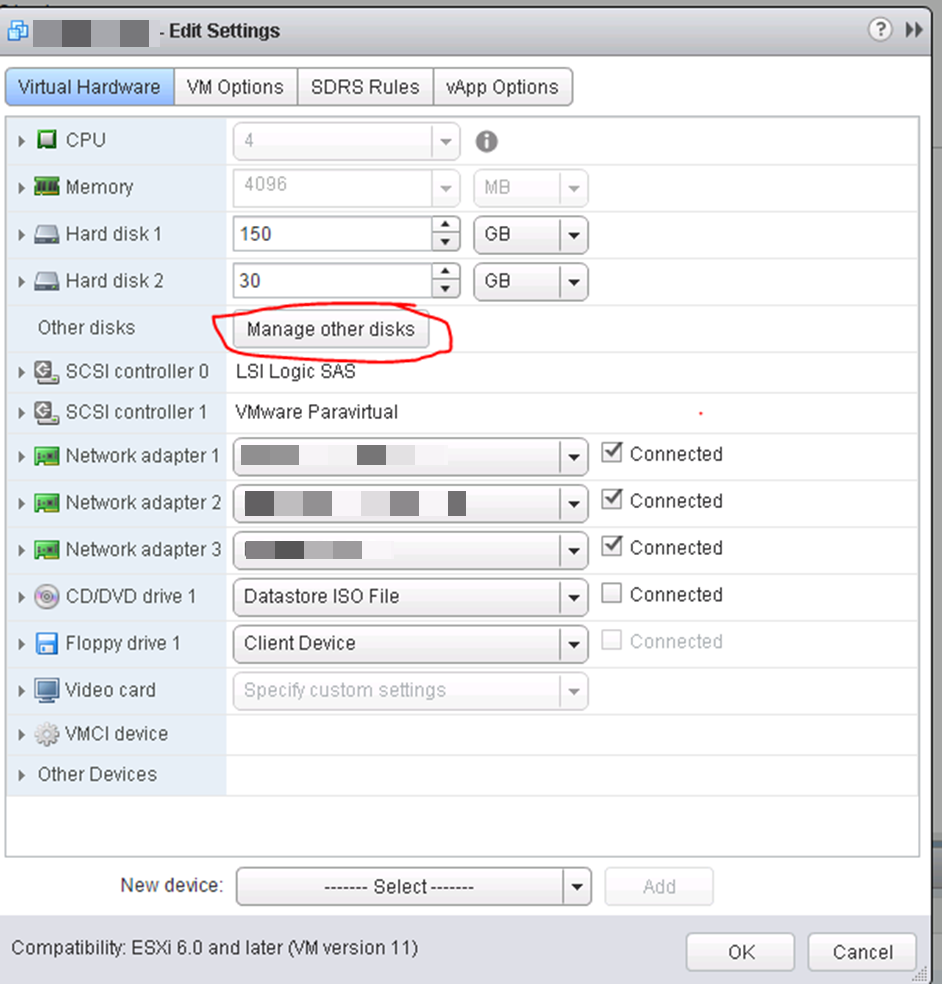
Open that button, then drop down the details on the disk you’re looking at and it will show you the VMDK and datastore. This VMDK is just a “pointer” or “mapping” file to the LUN.
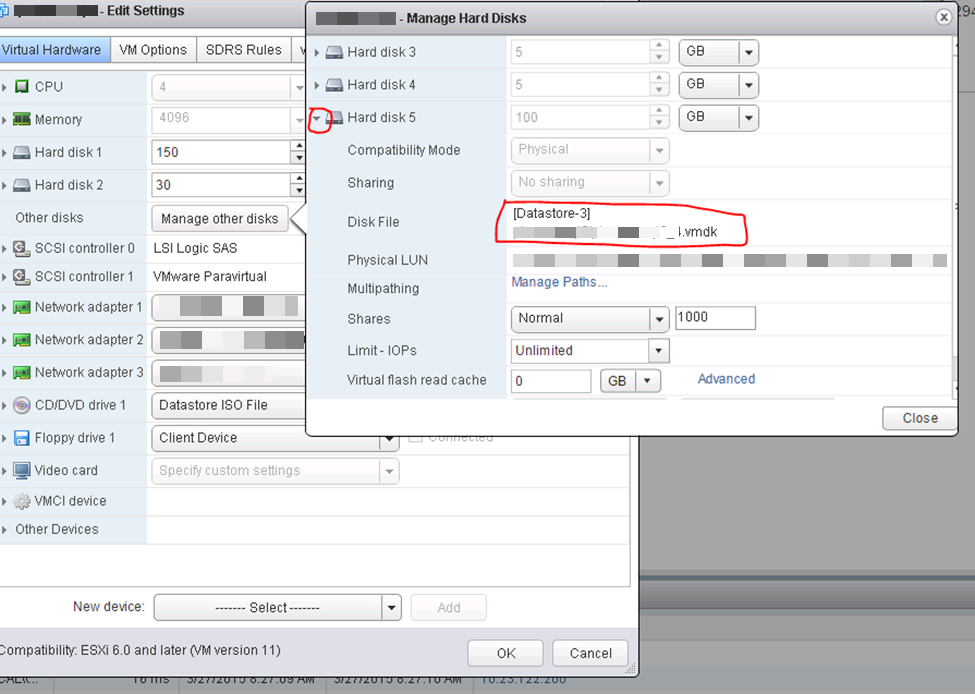
Pick the SAME SCSI controller and port that you did on A;

ISSUES ENCOUNTERED;
Set LUNS as “perennially reserved”. If this is not set right, the ESX HOST will take HOURS to boot, depending on how many RDMs it has to scan. Ours took 2.75 to boot. When this was set right via esxcli, they would boot in about 6 minutes, counting the HP specific boot processes. This is addressed in this KB, scroll down to the “perennially reserved” section. ESXi/ESX hosts with visibility to RDM LUNs being used by MSCS nodes with RDMs may take a long time to start or during LUN rescan (1016106)
EXPANDING RDM sizes.
PARAVIRTUAL driver
Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) Configure High Availability – Study Guide
These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
All, or nearly all, sections include DEMOS so I’m not notating that separately.
- Configure Network Load Balancing
- most commonly used with IIS
- stateless (doesn’t matter what node user connects with)
- Configure NLB Prerequisites
- install Feature
- Unicast, Multicast, IGMP Multicast
- Unicast
- always works
- 1:1
- requires a second NIC on each server
- causes subnet flooding; all traffic to all hosts goes to all hosts
- Multicast
- no second NIC
- network configurations
- does not solve subnet flooding
- IGMP Multicast – best practice
- no second nic
- network requirements
- solve subnet flooding problem
- Install NLB Nodes
- Configure Cluster Operation Mode
- Configure Port Rules and Affinity
- Upgrade an NLB Cluster
- Configure Failover Clustering (read prior post here)
- Cluster Storage
- shared storage is not built in Windows; it’s a foreign concept
- proper configuration of storage is critical
- iSCSI, FC, Storage Spaces (in our previous FS training)
- we’re using iSCSI here in this demo
- Configure Cluster networking
- best practice to separate cluster private network and storage network
- Failover Cluster Manager – console for cluster management
- Cluster Validation wizard (lots of experience with this 😉
- In this Demo, Cluster Private network, Storage network, and Management / Production
- Check the networks in Failover Cluster Manager
- Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) used by Hyper-V virtual machines
- Quorum (chosen by smallest size)
- Available Storage LUNs (if containing a VM, they all would have to fail over at the same time (or each have dedicated LUN)
- CSV, each VM can fail over individually
- you can define a disk as a CSV, and you can revert also.
- More here on Using CSV for Failover Cluster
- CSV cache size configuration; (Get-Cluster).BlockCacheSize = 512 for Server 2012 R2, for more read the link above.
- Quorum configuration
- Quorum is only to identify if enough of a cluster remains to still operate as a quorum.
- Quorum Models (dependent on number of nodes)
- Node majority (used for ODD number of nodes)
- Node and Disk Majority (even number of nodes)
- “split brain” when cluster breaks into two separate groups of nodes who each think they are quorum
- No Majority Disk Only (old, not used any more)
- Node and File Server Majority (special considerations) even nodes, multi site. The separate vote goes to a disk file share somewhere.
- Configure quorum model in Failover Cluster Manager
- MS automatically manages cluster quorum setting now. “use default quorum configuration”
- Or, you can go to advanced features and dance with the complexity on your own.
- Clusters without network names (detached cluster) Deploy an Active Directory-Detached Cluster
- SQL server outside your firewall
- not supported for several additional roles
- no bitlocker
- no CAU (Cluster Aware Updating)
- read the link
- cannot use FOCM
- PS – (Get-Cluster).AdministrativeAccessPoint
- read the link for more
- CAU (Cluster Aware Updating)
- “update cluster” item in Server Manager
- allows cluster to manage resource movement to update nodes/hosts.
- configure self-updating options wizard
- add the ROLE on the cluster
- choose schedule (normal WSUS stuff)
- reboot timeouts, max retries, pre or post scripts, recommended / important
- All the above is for Windows updates, not WSUS
- “Analyze cluster updating readiness”
- PS
- Restoring single node of cluster
- Evict = kicking node out
- restore configuration from backup (make sure you have system state)
- Upgrading a cluster
- not recommended to directly upgrade a cluster
- this is a cut and move
- “copy cluster roles” from a wizard from the TARGET cluster, connect to OLD cluster to get configs.
- Cluster Storage
- Manage Failover Clustering Roles
- remember MSCS is a “general purpose” clustering solution
- role-specific settings
- DFS, SHCP, DTC, FIle Server, iSCSI target, etc., etc..
- Generic application, script, or service
- DEMO – clustered NOTEPAD via Generic Application
- cluster is a SINGLE instance of the app that fails from node to node, moving the resources (including created drives) as needed
- Continuously available file server
- General Use, or SOFS (Scale Out File Server) (used for Hyper-V and SQL)
- Configure Virtual Machines
- do not put SOFS and VMs on same CSV
- fail-over and preferences
- ROLES (shared app, file server, VM, etc.)
- move, stop, change startup priority
- no autostart
- add resources or storage
- “show dependency” report
- graphical representation of dependencies
- “preferred owner” unchecked can be used, just not preferred
- failover max
- failback now/yes, set hours it can happen
- cluster handles DNS records for cluster required records
- you can manually add dependencies
- possible and preferred owners
- possible owners (cannot be on any node that is not checked)
- preferred owner (can use unchecked nodes, they’re just not preferred)
- guest clustering
- Manage VM Movement
- Migration – Live, Quick, Storage
- Quick
- the old fashioned, with a quick period of loss of service
- Live
- no loss of service
- Storage
- moving the .vhdx, the data
- Quick is technically faster, and uses less bandwidth than Live
- Live – procs need to be same manufacturer and similar family
- virtual switches needs to be named the same
- physical devices must be disconnected
- DEMO
- constrained delegation has to be configured to the hosts that you want to migrate to/from
- CredSSP alternative to Kerbos/constrained delegation but CredSSP requires you to log onto the machine to start the migration
- Quick
- Import, Export, Copy
- have to export/import if you can’t do quick/live migration
- Configure VM Health Protection
- move to locations without proper networks, or something similar
- VMHP is under Network Adapter / advanced features
- it will move it back to prior location if it ends up isolated
- ENABLED by default
- Configure Drain on Shutdown
- drain a node on shutdown
- ENABLED by default
- Configure VM Monitoring
- “resources” tab on bottome of Failover Cluster Manager
- checkbox to enable automatic recovery for application health monitoring
- if/when enabled, you can select services via checkbox that you want to include for application monitoring.
- Migration – Live, Quick, Storage
Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) Configure Active Directory – Study Guide
These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
- Introduction
- Not about the basics, this is 412 training so the basics should be in place
- Multiple Forests, multiple domains
- Configure a Forest or Domain
- Configure Trusts
- Configure Sites (remember from an era when WAN connectivity and site replication was expensive)
- Manage Active Directory and SYSVOL Replication
- RODC
- Configure a Forest or Domain
- implement multi domain and multi forest AD, with interoperability with previous versions of AD.
- Upgrading existing domains and forests, including preparation and functional levels
- Configure multiple UPN suffixes
- Used to require contiguous namespace; contoso.com, denver.contoso.com, paris.contoso.com.
- now we can use DISJOINTED namespaces. can have a forest with the following domains;
- contoso.com
- denver.contoso.com
- widget.com
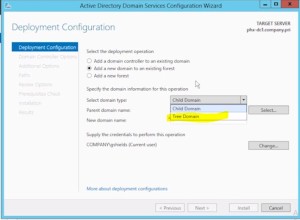
- This is called a TREE DOMAIN (as in “forest”, “trees” I suppose….) vs. the old
CHILD DOMAIN
- now we can use DISJOINTED namespaces. can have a forest with the following domains;
- When would you want to use a multi domain structure (desired state now is to minimize)?
- habit essentially
- political or organizational
- Autonomy (separation)
- Data isolation
- Segregation for replication /authentication /authorization
- SECURITY is not one of the reasons as part of the same forest.
- Multi Forest structure
- when two forests merge (purchase a company, etc.)
- two forests connected by a TRUST of some sort.
- Trusts require MANUAL creation
- Different requirements for AD Schema can dictate multiple Forests
- Exchange Organizations (In Exchange, only allowed one, so if your Exchange needs require more, then you are multi forest)
- Permissions required for creation
- To build a new forest, Local Admin on first DC (there is no AD yet)
- To build a new domain tree or child domain, you must be Enterprise Admin
- To add additional DCs, you must be a Domain Admin
- Upgrade Process for Domain or Forest (know this process)
- get healthy (make sure everything is working right)
- extend the schema (essentially adding columns to AD database, or new characteristics or fields) (ADPREP)
- upgrade DCs to new OS (all DCs need to be upgraded prior to raising functional level). Hopefully you don’t have hundreds of DCs.
- relocate FMSO roles if needed
- raise domain/forest functional level
- DEMO – extend schema
- adprep (link above)
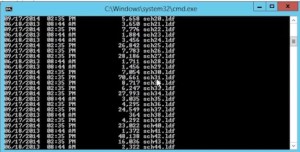
- uses the stack of .ldf files where adprep resides
- remember you can view these attributes in the ad database using ADSI Edit.
- adprep
- first use /forestprep
- then /domain prep
- optionally /gpprep, and /rodcprep
- now raise the functional level
- ad domains and trusts
- cannot go backwords, this is a one way road.
- What’s new in the functional levels
- Creating new UPN suffix
- AD Domains and Trusts, UPN suffixes
- add what you want in AD D and T
- then in ADUC you can use them in the user account tab
- adprep (link above)
- Configure Trusts
- Configure External, Forest, Shortcut, Realm
- Configure trust authentication
- Forest wide, or “selective”
- Configure SID filtering
- Get-ADUser -filter * | select SAMAccountName,sid (returns SIDS for users)
- SID filtering is on my default in external trusts.
- used in domain object migrations (from domain to another)
- has to be turned OFF to migrate (only time you would do this)
- SID history has to be ENABLED to migrate objects, which requires turning off SID filtering. Example; move a user to different domain, if you don’t do this properly a new SID is created and they lose access to printers they used prior. With SID history ENABLED, user object retains a history of both SIDs
- Detailed explanation and example of disabling SID filtering, enabling SID history here.
- Configure Name Suffix Routing
- determine what name suffixes get passed / routed to other side of trust
- Fundamentals
- trusts have direction – trusting, vs. trusted
- the direction is opposite of the direction of access
- remember by “wing it” is ‘eng -> ‘ed. From trustING to trustED.
- most are bi-directional
- can be transitive (if A trusts B, and B trusts C, then A trusts C)
- different types
- External from one domain in one forest to domain in a different forest
- Shortcut – literally a shortcut to another domain in same complex forest. Not common as AD simplifies
- Forest – between two forest roots; everything in forest is trusted. Transitive. Most common type of trust. Acquisitions. Always transitive. Can configure rules of authentication.
- Need name resolution to set up. Can be done by consolidating nameservices. In larger environment, conditional forwarders.
- create from AD Domains and Trusts
- can create both halves of trust from one side (one server)
- Realm trust – to non-AD Kerberos realm / Linux
- Configure Sites
- Created for AD replication across geographical locations
- Associated with subnets (VYOS router for lab)
- KCC (knowledge consistency checker)
- Configure Sites and Subnets
- rename “Default-First-Site-Name”, use it and create additional as needed
- create subnets and associate to sites
- Create and Configure Site Links
- Inter-Site transports
- most of the time is IP, NOT SMTP
- all sites are added to IP default site link
- absolute value of the cost is meaningless, only the RELATIVE value (compared to other links) has meaning
- A lot of this had more meaning when network connectivity was expensive and low capacity
- Manage Site Coverage
- you need a DC in each site
- are the DCs Global Catalogs (old times was limited due to processing power, bandwidth)
- now best practices are simply make every DC a GC
- if multiple DCs in a site, define a preferred BridgeHead server. Or leave this alone and leave it to KCC.
- best practice is leave it to KCC
- Manage Registration of SRV Records
- determines what DC site computers use
- ipconfig -registerdns make the DC set srv records
- Move DCs Between Sites
- Manage AD Replication and SYSVOL replication
- Upgrade SYSVOL replication to DFS-R (Distributed File System Replication)
- If you have an old, upgraded, AD, you might not be on DFS-R and still on the old FRS (File Replication Service)
- upgrading to DFSR
- three steps after get healthy, migrate to prepared state, migrate to redirected state, migrate to eliminated state
- dfsrmig /? (powershell for DFSR migration)
- dfsrmig /getglobalstate
- results will be “prepared”, “redirected”, or “eliminated”
- only do one step at a time then WAIT
- Some health check commands
- gwmi – class win32_logicaldisk – ComputerName yourcomputername (shows drive space)
- repadmin /syncall /force /aped (forces domain sync and ignore all schedules)
- update-DfsrConfigurationFromAD
- Configure replication to RODCs
- single use case; unsecure branch location. only contains passwords and content for that branch
- never log onto RODC with privileged account
- delegated RODC administrator (the selected group can administer the RODC (“managed by” tab)
- Configure password policy replication for RODCs
- set policy for which PWs you want to cache on RODC (password replication TAB)
- you can see what users/computers are replicated to RODC on “advanced” tab.
- Monitor and manage replication
- sites and services – right click and “replicate now” from AD Sites and Services
- repadmin /replicate server1 server2
- repadmin /showrepl
- repadmin /kcc
- repadmin /prp view servername reveal (shows RODC replication)
- in GPMC, look at a domain, you can see replication status
- dfsdiag
- nltest (tests if you can locate a DC)
- AD Change Notification (replicates to all sites instantly)
- ADSI edit
- sites
- “options”, from blank to “1”, now replicates across sites at same replication as intrasite replication.
- Upgrade SYSVOL replication to DFS-R (Distributed File System Replication)
Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) MCSA and the 70-412 Exam – Study Guide Part 2 – build a lab
These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
As mentioned previously, the second section of this course seem like it was going to focus on how to build a lab in preparation for training, so I broke it into a separate post.
Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) MCSA and the 70-412 Exam
Building Your 70-412 R2 Environment
- VMware workstation
- please note; VM Workstation is a licensed product; you have to PAY for it. You can get a 30

My physical lab 5 DL380 G5s (one not in picture) and two DL360 G5s. The G4s are being decomissioned.
day trial of VM Workstation here. Also, if you have ever passed a VMware certification (like me) then you get a free license as one of your benefits. So, for example, I have a permanent license for Workstation 10, but cannot upgrade without buying a new license. I suppose you could do this lab on VBOX also if you have familiarity there. At the end of this I will also post some links to good sites about virtual labs.
- please note; VM Workstation is a licensed product; you have to PAY for it. You can get a 30
- VM infrastructure and IP scheme
- Forest infrastructure
- Understanding the Network Infrastructure
- VyOs router for network routing
- Use of templates or clones. Discussion of Linked Clones to minimize disk use. Linked Clones are a VMware specific ability. VMware Linked Clones use the same virtual disks as the parent. So you could have 10 linked clones using one set of disks, with a very much improved storage use scenario especially in a lab.
- Reviewing lab IP scheme and host design;
- 4 Domain Controllers
- 1 File Server
- 2 NLB hosts
- 5 Failover Cluster hosts
- 1 Certificate server
- 1 RMS (Rights Management Server)
- 1 ADFS (Active Directory Federation Services)
- 1 desktop
- Total of 1,2,3 let’s see 16 machines looks like all in VM Workstation running on one PC
- Forest infrastructure
- company.whatever
- separate forest to test ADFS
- three different sites
- 4 subnets; VMware Workstation doesn’t support subnetting which is why we have VyOS
- Setting up VYOS
- default username and pw is “vyos”
- setting up multiple NICs to support the subnetting
- adding 4 more NICs
- Configured VYOS
- Configured internal home router for the appropriate vlans
Ok that’s about it. It does looks like a pretty good way to set up this all in a virtual lab. I’d like to see how it performs but probably pretty well since he put all the drives on a separate SSD.
Here are some of the other links I have gathered on building a lab. Some focus on low power (electricity costs), some focus on being quiet (don’t need the disturb the spouse) and some on different things. I’ve had the good fortune to be able to collect some HP G5 servers which I have been able to use, using iSCSI and / or VMware VSAN for storage. I used this lab to study for and pass my VCP-DCV5.1 test.
Links;
Labs in general
While this one could go under “low noise” or “low power” they’re not really stated goals so I’m putting it here, it’s one of the best; http://packetpushers.net/vmware-vcdx-lab-the-hardware/
Similar lab build; http://rickmur.com/home-lab-server/
A more expensive ($3,000.00) work office targeted option using HP / CDW parts; (can this run ILO?) https://virtualizationreview.com/blogs/virtual-mattox/2012/03/build-cheap-screaming-virtualization-lab-server.aspx
Another good follow along lab; http://ethancbanks.com/2014/03/15/my-home-lab-esxi-5-5-server-build-and-the-logic-behind-it-all/ but this guy had a couple of Cisco SG300-52 switches that are worth min $400.00 each so not really cheap.
Nested / Low Power / Low noise or some combination
“nested” generally simply means you have one hypervisor running on another, or one hypervisor running as a VM.
Nested lab on VMware Workstation; low cost; http://www.heathreynolds.com/2014/02/building-nested-esxi-lab-on-vmware.html
Nested lab on ONE DL380 G5; http://www.running-system.com/how-to-build-a-nested-lab-on-a-hp-dl380-g5-server-step-1/ You can sometimes get a G5 on Craigslist for cheap or free. I got a couple for free, and I got a couple for as little as $90.00. There are thousands of these G5s still in production and they are solid hardware. Anything older than G5 won’t have processors that will support virtualization.
First one I have seen specifically on VMware 6.0 which just came out a few months ago; http://www.vladan.fr/nested-esxi-6-in-a-lab/
This looks cool; Intel NUC, low power (15w with 5 running VMs) http://www.vclouds.nl/how-to-build-a-low-cost-low-power-and-fast-esxi-home-lab/
Around 30w; https://matthill.eu/projects/vmware-esxi-low-power-home-lab/
VBOX lab
http://pc-addicts.com/building-the-ultimate-virtualbox-lab-intro/
In my experience, Memory is going to be the first constraint on a lab system no matter which method you choose. After that, probably storage. On nested environments (like this Pluralsight training) SSD would be a great idea.
Windows Server 2012 R2 (70-412) MCSA and the 70-412 Exam – Study Guide
These notes are my personal notes from the FREE training on Pluralsight. You can get your FREE signup through technet/MSDN or Dreamspark. The title of this course is exactly the title of this post. These notes are from this specific course only. I use these as a refresher Study Guide. POWERSHELL topics and  cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
cmdlets are in purple. I have a few notes with the “DEMO” each time the training included a DEMO just so you can see how many demos there were which were really helpful. Thanks to Greg Shields @ConcentratdGreg, the trainer, contact info at the end.
After doing the Advanced Features training, I’m expanding into the rest on Pluralsight and will go through as many as I can before my test date. This content should also apply to the 70-417. The 417 is the one I’m taking is a combination of 410, 411, and 412 all in one. It breaks down the score for each section. You have to pass all three sections. I have passed two of them (410 and 411) but not the 412, so if you fail one of them, you fail the entire test.
- An Introduction to the MCSA’s Final Exam

- bunch of stuff about exam, objectives, strategy
- 417 is a combination of 410, 411 and 412
- Intended audience; ok.
- Without taking a bunch of notes, let’s just say review the exam objectives, just scroll down on the appropriate page for the specific exam you’re looking at;
- R2 specific information has been included since January 2014. So, while I don’t think you’ll have a lot of questions about the differences from 2012 and Server 2012 R2, I WOULD expect to know the new Server 2012 R2 features.
- Link on what is NEW in Server 2012 R2
- The next section is titled Building Your 70-412 R2 Environment
- I’m going to put the next section in a new post focused on how to build a lab.